types of reactions ch 11
advertisement

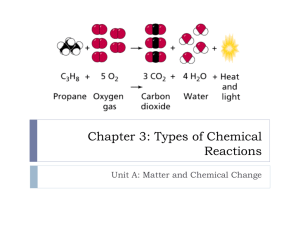
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions 11.1 Chemical Reactions Reactants: starting material in a chemical reaction Products: substance formed in a chemical reaction → : arrow means “yields” 11.1 cont + : plus sign means “and”, separates products and reactants Law of conservation of mass: in any chemical or physical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed. 11.1 Writing Chemical Equations Skeleton equation: a chem. rxn that does not indicate the relative amounts of the reactants and products Chemical Equations: describe what occurs in a chemical reaction. Reactants on left ~ arrow ~ Products on right Catalyst: a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction w/o being used up. (written on top of arrow) 11.1 cont. Symbols used in chemical equations → - “yields” + - “and” (s) – solid reactant or product (l) – liquid reactant or product (g) – gas reactant or product (aq) – aqueous solution, reactant or product → heat → Elec. → H2SO4 11.1 Balancing Equations Balancing Equations: has equal numbers of the same type of atom on both sides of the equation Whole number coefficient: used to balance equations 11.2 Types of reactions Combination reaction: two or more substances react to form a single substance Decomposition reaction: single compound is broken down into two or more products Rxns cont. Single-replacement: atoms of one element replace the atoms of another element in a compound Double-replacement: involve an exchange of positive ions between two compounds Combustion: an element or a compound reacts with oxygen, often producing energy in the form of heat and light. (FIRE!!) 11.3 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Complete ionic equation – shows dissolved ionic compounds as dissociated free ions. Spectator ion – an ion that appears on both sides of a complete ionic equation and is not directly involved in the reaction 11.3 cont Net ionic equation – an equations for a reaction in solution that shows only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change.