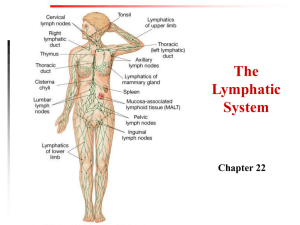
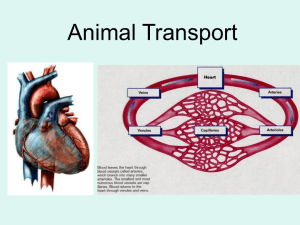
Human Immune System I. Pathogens Definition
advertisement

Human Immune System I. Pathogens Definition ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Examples ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… II. First Line of Defense is ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… BARRIERS a. skin …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. b. airways ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… c. reflexes ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. d. normal flora ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… e. blood clotting ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. CHEMICALS a. sebum ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. b. lysozyme ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… c. acids …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. What are the easiest ways for pathogens to enter the body? …………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………..……………………………………………………………………………………………… III. Second Line of defense is …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE 1. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. Chemicals released from ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Chemicals are: …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. Histamine causes …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. Protaglandins cause ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5. Kinins ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6. ………………………………………………. leave the blood vessel. 7. Bacteria are eaten by: …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 8. Pus is …….……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9. Tissue repaired. What is the purpose of histamine? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. FEVER 1. …………………………………………………… resets the body thermostat. 2. Heat comes from …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… How does this help fight infection? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… COMPLEMENT PROTEINS 1. …………………….. types 2. functions ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. INTERFERON 1. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. Warns nearby cells of the virus. 3. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. PHAGOCYTES or …………………………………………………………………………… Types: ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ANTIGENS are ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Epitope ………………………………………………………… MHC ……………………………………………………………… MHC 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… MHC 2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Why is this important? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. NATURAL KILLER CELLS 1. Kills cells ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. Destroys them because they do not ……………………………………………………………………………………… 3. DOES NOT …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. but can ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… EOSINOPHILS Kill ……………………………………… by …………………………….……………………………………………………………… Describe the function of each cell pictured above. Why was the analogy of a mine field used to describe the second line of defense? ………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. IV. Third line of Defense is …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Unique to ………………………………………………. Uses cells called ……………………………………………. Which come from the …………………………………………………….. B cells ………………………………………………………………………………………………. T cells ………………………………………………………………………………………………. Lymphoid tissue Primary …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Secondary …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………………….. Lymph vessels …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Lymph nodes …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. What are the two major purposes of the lymphatic system? …………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Lymphocytes Contain ……………………………………………….. sites ……………………………………………………………………….. of different types Cell Mediated Immunity T cells Four types 1. Helper T cell ………………………………………………………………………………………… Makes ………………………………………………………………….. Activate …………………………………….. and ……………………………………….. This results in …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Helper T cells also make …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 2. Cytotoxic T cell eliminate ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. And cells with ……………………………………………… Also make …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 3. Memory T cells remain in the ……………………………………….. and are ready to …………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Live for …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4. Regulatory T cells used to …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. die off leaving memory cells How do cytotoxic T cells compare to natural killer cells? ………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Humoral Immunity B Cells 2 types Naïve B cell activated by ………………………………………………… or ………………………………………………………..………. Begins cloning, become plasma cells Plasma B cells make and release …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. which are all ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. The antibodies attach to ………………………………………………………………. Bacteria are ………………………………………………………….. making it easier to find them Viruses are ……………………………………………………………… so they cannot enter cells Memory B cells are created Memory Cells ……………………………………………… up second response to the pathogen ……………………………………………… total number of antibodies Antibodies Are …………………………… with …………………………………………………………………. Can be either ………………………………………………….. or ……………………………. ……………………………………………. Bond to ……………………………………………… Come in …………… types IgG IgA IgM IgD IgE What part of the antibody attached to the pathogen’s antigens? ………………………………………………………………………… Antibody Variability V section …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. D section …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. J section …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. Recombination means …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Recombination and mutations result in ……………………………………………….. possible combinations. Why is it important to have so many types of antibodies? ……………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Autoimmunity Immune system …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Examples ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Types of Immunity Natural ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Artificial ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Active …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Passive ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1. …………………………… 2. …………………………… 3. …………………………… 4. …………………………… Allergies First exposure: Immune system reacts slowly as no ………………………………….. cells exist for this antigen. Second exposure: ……………………………. antibodies have been attached to ………………………………. cells. When antigen bonds to …………………………. antibodies on mast cell, ……………………………..…….. is released. What does histamine do? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Why was the third line of defense illustrated with a smart bomb? …………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………