WHAT TO STUDY – Immune System
advertisement

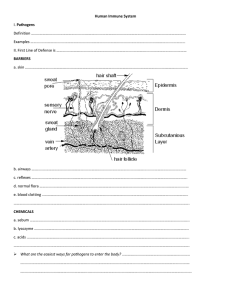
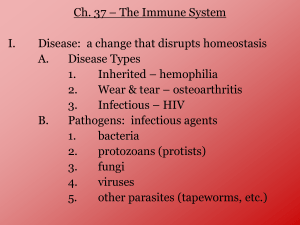
WHAT TO STUDY – Immune System Immune System: helps protect the body against disease Pathogens: disease-causing microorganism (virus, bacteria, fungi, etc…) Antigens: proteins found on the surface of a pathogen - Triggers an immune response (production of antibodies) Antibodies: proteins that help destroy pathogens - Produced when an antigen enters the body - Bind to antigens whose shape matches (PERFECT FIT) Two Types of Immunity 1. Active immunity: permanent/long-term a. By getting and recovering from the disease b. By getting a vaccine (dead or weak form of pathogen - 2. Passive Immunity: short term a. By receiving an injection of antibodies b. Baby receives antibodies from mom in uterus before birth c. Baby receives antibodies from mom through breast milk Body produces antibodies and memory cells Antibodies attach to antigens to help destroy pathogen Memory cells remain in the blood to “remember” the pathogen Disease Infectious disease: can be transmitted (caused by a pathogen) - AIDS: caused by the HIV virus o HIV virus weakens the immune system body can no longer fight pathogens o Transmitted by: Contact with infected blood Sharing infected IV needles Sexual contact with an infected person Non-infectious disease: not caused by a pathogen - Allergies: body overreacts to a HARMLESS substance o Histamines: chemical that causes the allergic reaction - Autoimmune disease: the immune system attacks your own body cells - Cancer: abnormal and uncontrolled cell division o Can lead to production of tumors