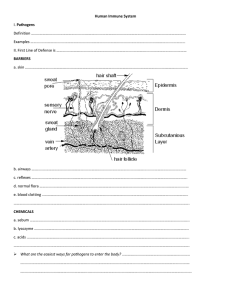
2. Immune System WEB
advertisement
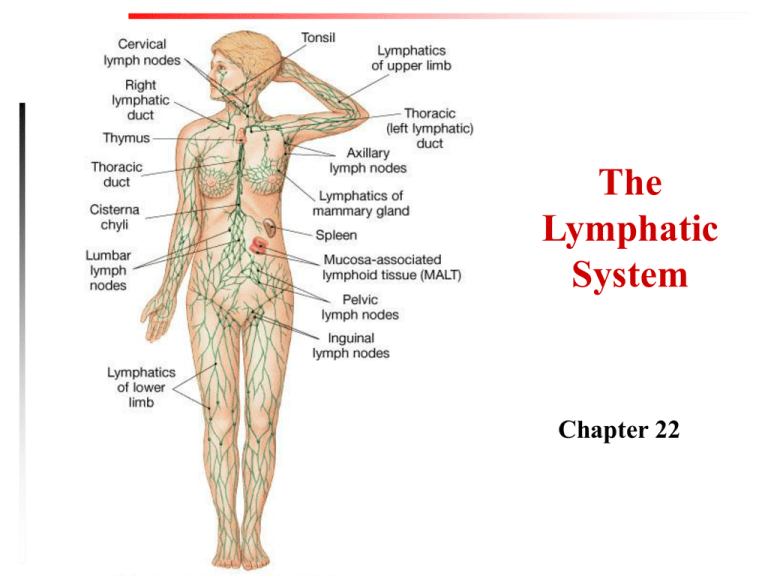
The Lymphatic System Chapter 22 Immune System • Defends body against pathogens (bacteria, viruses, some protists & fungi) • Distinguishes between self and non-self • Infectious Diseases – result from the presence of pathogens • Transmission includes contact with infected individuals/organism, water, food, or airborne inhalation • Contagious (Communicable) Diseases infectious diseases capable of being transmitted from one person to another 1. First line of defense (non-specific) • Skin • Lysozyme = enzyme in saliva, sweat, tears; attacks bacterial cell walls • Mucus = traps pathogens • Cilia = help clear mucus (and pathogens) from respiratory tract 2. Second line of defense (non-specific) A. Phagocytic white blood cells (mainly neutrophils and monocytes) destroy pathogens (phago= eat, cyte=cell) • Attracted to a site of infection by chemicals released by injured cells (chemotaxis) B. Inflammation - infected cells release histamine which is a vasodilator, this causes swelling, redness, pain, fever, and it brings WBCs to the area of infection antibody immunity; specific rd Line of 3 attack on foreign particles Defense (specific) Antigen - foreign protein that triggers immune response Antibodies (immunoglobulins) proteins made by lymphocytes; bind to antigens and mark them for macrophage destruction Lymphocytes - WBCs; two types: B (mature in bone marrow) and T (mature in thymus); both are made in bone marrow Look at this picture – p. 801 3rd Line of Defense Cont. 1. Primary Immune Response • First appearance of antigen in the body; memory cells are formed 2. Secondary Immune Response • Second appearance of antigen; higher levels of antibodies are formed in shorter time; you do not experience sickness due to antibody production from memory cells Treatment of Infectious Diseases 1. Three lines of defense of the Immune System 2. Antibiotics (ONLY FOR BACTERIAL INFECTIONS!!!) • First antibiotic – penicillin – Alexander Flemming 3. Vaccines • Activate the primary immune response and formation of memory cells without causing severe disease symptoms • Typically made from dead/inactive virus or bacteria or their proteins • First vaccine – smallpox – Edward Jenner Disorders of the Immune System • Autoimmune Disorders – body produces antibodies against its own tissue, e.g. Grave’s disease (hyperthyroidism) and rheumatoid arthritis • Allergies occur when the body reacts to materials which should not be antigenic, e.g. peanuts Immunity Active immunity Production of a person’s own antibodies; long lasting Natural Active When pathogen enters body in the normal way, we make antibodies Passive immunity An individual is given antibodies by another ; short-term (weeks- 6 months) Artificial Active Natural Passive Vaccination – From mother in person makes uterus & breast milk antibodies without becoming ill Edward Jenner Artificial Passive Immunoglobulin injection; extremely fast, but short lived (e.g. snake venom)