Defense Notes
advertisement

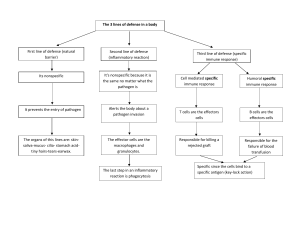
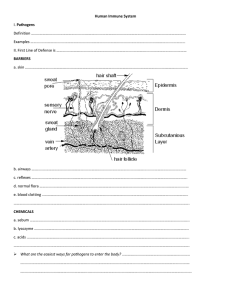
Defense from Illness or Injury Defense against Disease/Illness Germ Theory of Disease Disease is caused by pathogens Examples: bacteria, fungi, protists, viruses Spread by: physical contact, contaminated food and water, infected animals Nonspecific Defense -does not discriminate between one threat and another; includes physical and chemical barriers First Line of Defense – keep pathogens out of the body Skin (the most important nonspecific barrier to disease) Secreted Fluids (mucus, tears, saliva) Second Line of Defense – the Inflammatory Response Patrolling cells & proteins attack invaders that penetrate body’s outer barriers Triggered by tissue damage Increased blood supply delivers extra white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets, and clotting agents Causes inflammation – swelling, redness Fever helps the body fight infection by increasing temperature and raising heart rate Specific Defense – specific to the threat Third Line of Defense – the Immune Response Triggered by antigens (foreign invader; pathogen) Antibodies bind to specific antigens (your body either makes antibodies to fight the antigen or already has the antibodies required) o Each antibody is unique to match a particular antigen A good immune system has specificity, diversity, memory, and the ability to distinguish self from non-self Outside Help 1. Vaccination – the immune system is exposed to a harmless version of a pathogen a. Vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies so there will be a rapid response if there is a future exposure to the antigen b. Vaccines are particularly useful to prevent viral disease; also used for bacterial and fungal disease, but not as effective c. Jenner used the first successful vaccine (to prevent smallpox) 2. Antibiotics – drugs that combat living cells by interfering with various cellular functions a. Penicillin, the first antibiotic used, was discovered by Alexander Fleming by accident Antibiotics only work on things that are made of cells: bacteria, protists, fungi. They don’t work on viruses. Defense against Injury (Healing) Healing happens in overlapping stages. 1. Hemostasis – Platelets in blood stick to the injury and to each other, forming a clot to slow and stop bleeding 2. Inflammation – White blood cells clear out damaged or dead body cells and also work to remove bacteria or other debris. 3. Proliferation (growth of new tissue) – Cells around the wound divide, forming new cells. Cells pull together, helping to close the wound. 4. Maturation (remodeling) – Alignment of cells to resume original shape/condition. Unneeded cells undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death.)