Immune System BINGO - answer sheet
advertisement
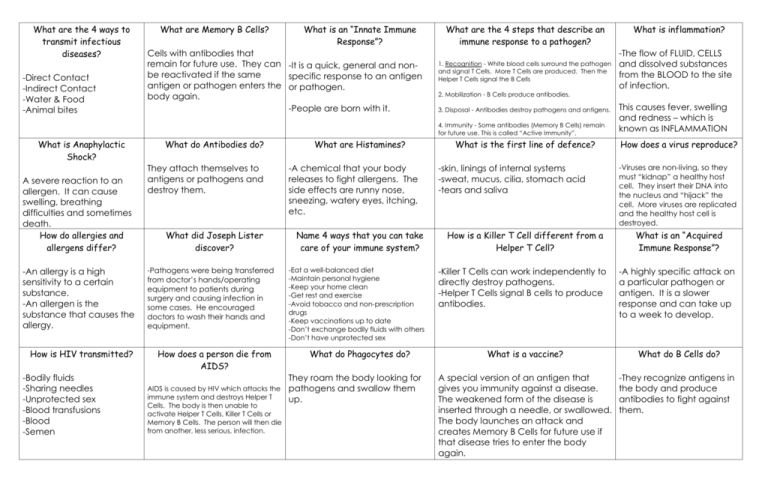
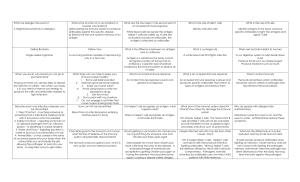
What are the 4 ways to transmit infectious diseases? -Direct Contact -Indirect Contact -Water & Food -Animal bites What are Memory B Cells? What is an “Innate Immune Response”? Cells with antibodies that remain for future use. They can -It is a quick, general and nonbe reactivated if the same specific response to an antigen antigen or pathogen enters the or pathogen. body again. -People are born with it. What are the 4 steps that describe an immune response to a pathogen? 1. Recognition - White blood cells surround the pathogen and signal T Cells. More T Cells are produced. Then the Helper T Cells signal the B Cells A severe reaction to an allergen. It can cause swelling, breathing difficulties and sometimes death. How do allergies and allergens differ? -An allergy is a high sensitivity to a certain substance. -An allergen is the substance that causes the allergy. How is HIV transmitted? -Bodily fluids -Sharing needles -Unprotected sex -Blood transfusions -Blood -Semen What do Antibodies do? They attach themselves to antigens or pathogens and destroy them. What did Joseph Lister discover? -Pathogens were being transferred from doctor’s hands/operating equipment to patients during surgery and causing infection in some cases. He encouraged doctors to wash their hands and equipment. How does a person die from AIDS? AIDS is caused by HIV which attacks the immune system and destroys Helper T Cells. The body is then unable to activate Helper T Cells, Killer T Cells or Memory B Cells. The person will then die from another, less serious, infection. What are Histamines? -A chemical that your body releases to fight allergens. The side effects are runny nose, sneezing, watery eyes, itching, etc. Name 4 ways that you can take care of your immune system? -Eat a well-balanced diet -Maintain personal hygiene -Keep your home clean -Get rest and exercise -Avoid tobacco and non-prescription drugs -Keep vaccinations up to date -Don’t exchange bodily fluids with others -Don’t have unprotected sex What do Phagocytes do? They roam the body looking for pathogens and swallow them up. -The flow of FLUID, CELLS and dissolved substances from the BLOOD to the site of infection. 2. Mobilization - B Cells produce antibodies. 3. Disposal - Antibodies destroy pathogens and antigens. 4. Immunity - Some antibodies (Memory B Cells) remain for future use. This is called “Active Immunity”. What is Anaphylactic Shock? What is inflammation? What is the first line of defence? -skin, linings of internal systems -sweat, mucus, cilia, stomach acid -tears and saliva How is a Killer T Cell different from a Helper T Cell? -Killer T Cells can work independently to directly destroy pathogens. -Helper T Cells signal B cells to produce antibodies. This causes fever, swelling and redness – which is known as INFLAMMATION How does a virus reproduce? -Viruses are non-living, so they must “kidnap” a healthy host cell. They insert their DNA into the nucleus and “hijack” the cell. More viruses are replicated and the healthy host cell is destroyed. What is an “Acquired Immune Response”? -A highly specific attack on a particular pathogen or antigen. It is a slower response and can take up to a week to develop. What is a vaccine? What do B Cells do? A special version of an antigen that gives you immunity against a disease. The weakened form of the disease is inserted through a needle, or swallowed. The body launches an attack and creates Memory B Cells for future use if that disease tries to enter the body again. -They recognize antigens in the body and produce antibodies to fight against them.