Simple Animals
advertisement

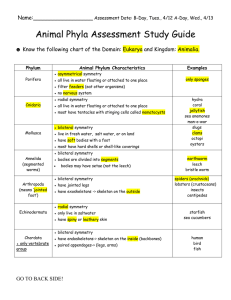
THE ANIMAL KINGDOM Characteristics of ALL Animals… • Multi-cellular •Eukaryotic (nucleus) •Consumers •Mobility PART 1: Simple Animals 1. SPONGES: • Most simple of all animals • Feed, breathe, and eliminate waste through pores • Traps what it needs as water flows thru • Sexual and asexual reproduction 2. STINGING-CELL ANIMALS • • • • Animals have stinging tentacles Sexual reproduction Have “mouth” structure Radial symmetry Anemone Jellyfish Hydra Symmetry • Radial Originates from a center point • Bilateral Divided into 2 equal sides 3. Flatworm • Flat in shape • Bilateral symmetry • Cephalization – “head” structure • Example: a. Tapeworm – Parasitic – Intestines – Can be very long b. Planaria – non-parasitic – found in freshwater – mouth/anus same structure 4. Roundworm • • • • Round in shape Separate mouth and anus Bilateral symmetry Example: – Ascaris • Parasitic roundworm • Causes death in 3rd world countries 5. Segmented Worms • Body divided into “segments” • Live anywhere (land, fresh + salt water) • Examples: Earthworm Leech • • • • 6. Soft-Bodied Animals (a.k.a. Mollusks) Soft body Usually protected with a hard shell Muscular foot for movement Examples: clam, oyster, scallop, slug, snail octopus