File
advertisement

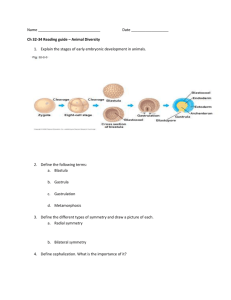
Animal Diversification 1. All animals: a) are heterotrophic; they eat other animals. b) share a common ancestor. c) reproduce sexually d) have a backbone. e) Only a) and b) are correct. 2. Which of the following is FALSE? a) Animals are multicellular. b) Animals do not undergo mitosis in the haploid stage. c) Animals eat other organisms. d) Animal cells lack cell walls. e) Animals are not all descended from a common ancestor. 3. Which of the following is NOT correct about all animals? a) All have true, defined tissues. b) All are descended from a common ancestor. c) All are multicellular. d) All are heterotrophic; they eat other animals. e) All are eukaryotes. 4. The most ancient branching point in the phylogeny of animals is the one that distinguishes between having: a) single cellularity and multicellularity. b) first gut opening develop into a mouth and first gut opening develop into an anus. c) growth by molting or by continuous additions. d) radial or bilateral symmetry. e) defined tissues or no tissues. 5. In the figure, animals that exhibit radial symmetry in the adult phase of their life cycle can be found in: a) all of the boxes. b) only in box III. c) only in box V. d) only in boxes I and II. 1 e) only in boxes I and IV. 6. Some general evolutionary change trends in animals include: a) larger body size, bilateral symmetry, and growth by continuous addition to skeletal elements. b) greater surface area to volume ratio, radial symmetry, diffusion to move nutrients in the body. c) lower surface area to volume ratio, radial symmetry, mutualism with photosynthetic organisms. d) radial symmetry, motility, filter feeding. e) bilateral symmetry, chitinous cell walls, ability to digest cellulose. 7. Most species of animals are: a) radially symmetrical. b) autotrophs. c) marine dwelling. d) invertebrates. e) carnivores. 8. Which of the following short descriptions best describes the body plan of modern sponges? a) an aggregation of cells built around a water canal system b) a complete gut with an anterior mouth and posterior anus c) a mouth connected to a blind sac in which digestion occurs d) a complete gut with one opening serving as both mouth and anus e) an aggregation of cells in a random arrangement 9. Sponges of the phylum Porifera are sessile, meaning that they: a) are parasitic and depend on their host for a constant supply of nutrients. b) reproduce asexually. c) have exoskeletons that they must shed as they grow larger. d) have both free-living and attached life stages. e) live attached to a solid structure and do not move around. 10. Members of which of the following groups exhibit radial symmetry? a) Porifera b) Cnidaria c) Platyhelminthes d) Nematoda e) Mollusca 11. Segmented worms (annelids), roundworms (nematodes), and flatworms (platyhelminths): a) make up a monophyletic clade. b) are all asexual. c) are all internal parasites. d) are all bilaterally symmetrical. e) Only a) and d) are correct. 12. All arthropods have: a) antennae and compound eyes. b) a chitinous exoskeleton and jointed appendages. c) development through metamorphosis d) stinging mouth parts. e) Only b) and c) are correct. 2 13. Echinoderm larvae are ________________, while echinoderm adults are ________________. a) radially symmetrical; bilaterally symmetrical b) gastropods; bivalves c) segmented; unsegmented d) aquatic; terrestrial e) bilaterally symmetrical; radially symmetrical 14. Name and describe the three characteristics of animals. 15. List and describe the four body structures common to all chordates. If humans are chordates, do we have these structures as well, and if so, where? 3