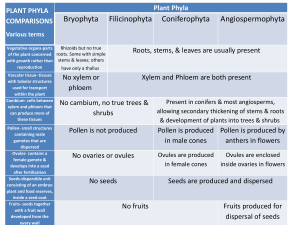
5.3 Classification of Biodiversity Use This Link to help you: https://ib.bioninja.com.au/standard-level/topic-5-evolution-and-biodi/53-classification-of-bio div/ A) Classification 1) Outline the binomial system of nomenclature and who invented it. The binomial system is a name system that is universally used and was made by linneaus 2) List the three domains of life and a few major characteristics of each. The three domains is archae bacteria and eukaryote 3) List the seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa, using examples from two different kingdoms starting with the domain. Taxa Plant Example Animal Example Domain Eukarya Eukarya kingdom Plantae animallia Magnoliaphyta chordata class Liliopsida mammalia order Asparagales primate family Amaryllidaceae homodae genus Allium homo species sativum sapien Garlic human phylum Common Name 4) Compare different methods of biological classification, and include advantages and disadvantages of each if relevant. Natural: this is where a genus along with its taxa has evolved from a common ancestor Artificial: They are grouped by basic characteristics and do not have evolutionary relationships Phylogenetic: Differentiation between species based on genes and dna B) Biodiversity 1) Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using external recognition features and method of reproduction. Bryophyta: No vascularisation, no roots, no stems, no leaves and it reproduces by producing spores from sporangia. It is anchored by rhizoid. Filicinophyta: There is vascularisation, roots, stems, and leaves and it reproduces spores from sori in cllusters. Leaves are pinnate Coniferophyta: It has vascularisation, roots, stems, and leaves and it reproduces by non motile gametes (seeds) in the cones. Stems are woody and leaves are waxy and needle like Angiospermophyta: It has vascularisation, leaves, roots, and stems, the seed is produce in the ovule in the flower. May have fruit 2) Construct a simple dichotomous key (diagrammatic) to identify the four plant phyla. 3) Distinguish between the following phyla of invertebrate animals, using external recognition features and include examples of each. Porifera: Asymmetrical with no mouth or anus, could have silica or calcium carbonate based for structure Cnidaria: Radial symmetry with a mouth but no anus, could have tentacles to sting for food Platyhelminthes: bilateral symmetry and has a mouth but no anus, has a flattened body shape Annelida: bilateral symmetry and has a mouth and anus, body is composed of ring segments Mollusca: bilateral symmetry has a searate mouth and anus, body composed of visceral math Arthropoda: bilateral symmetry and has a separate mouth and anus, jointed body sections 4) Describe the key characteristics of phylum Chordata Have bilateral symmetry Have a separate mouth and anus Have a notochord and a hollow, dorsal nerve tube 5) Distinguish between the following classes of vertebrate animals, using simple recognition features and method of producing offspring Fish: Covered in scales made out of bony plates in the skin, Reproduce via external fertilisation Amphibians: Moist skin, permeable to gases and water Reproduce via external fertilisation Reptiles: Covered in scales made out of keratin,Reproduce via internal fertilisation and females lay eggs with soft shell,Breathe through lungs that have extensive folds Birds: Covered in feathers (made out of keratin) Reproduce via internal fertilisation and females lay eggs with hard shells Breathe through lungs with parabronchial tubes Maintain a constant internal body temperature Mammals: Skin has follicles which produce hair made out of keratin, Reproduce via internal fertilisation and females feed young with milk from mammary glands,Breathe through lungs with alveoli,Maintain a constant internal body temperature 6) Construct a simple dichotomous key (descriptive) to identify the five vertebrate classes