Animal Phyla Assessment Study Guide Name:__________________
advertisement
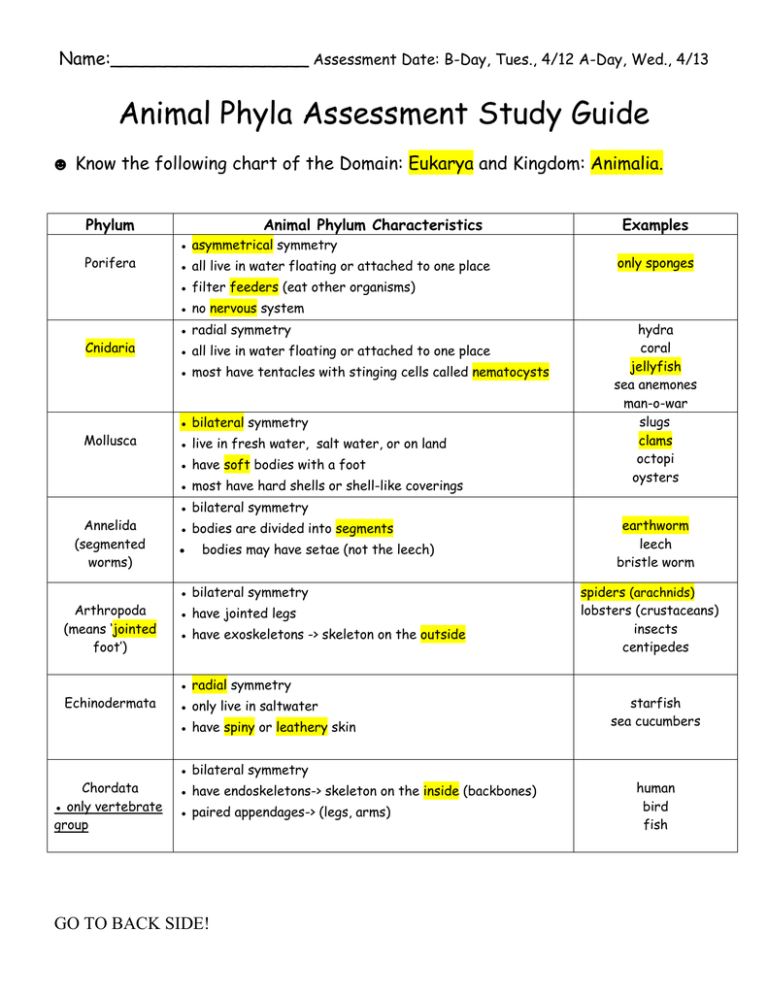
Name:__________________ Assessment Date: B-Day, Tues., 4/12 A-Day, Wed., 4/13 Animal Phyla Assessment Study Guide ☻ Know the following chart of the Domain: Eukarya and Kingdom: Animalia. Phylum Porifera Animal Phylum Characteristics ● asymmetrical symmetry ● all live in water floating or attached to one place Examples only sponges ● filter feeders (eat other organisms) ● no nervous system Cnidaria ● radial symmetry ● all live in water floating or attached to one place ● most have tentacles with stinging cells called nematocysts Mollusca ● bilateral symmetry ● live in fresh water, salt water, or on land ● have soft bodies with a foot ● most have hard shells or shell-like coverings Annelida (segmented worms) Arthropoda (means ‘jointed foot’) Echinodermata ● bilateral symmetry ● bodies are divided into segments bodies may have setae (not the leech) ● bilateral symmetry ● have jointed legs ● have exoskeletons -> skeleton on the outside ● radial symmetry ● only live in saltwater ● have spiny or leathery skin Chordata ● only vertebrate group ● bilateral symmetry ● have endoskeletons-> skeleton on the inside (backbones) ● paired appendages-> (legs, arms) GO TO BACK SIDE! hydra coral jellyfish sea anemones man-o-war slugs clams octopi oysters earthworm leech bristle worm spiders (arachnids) lobsters (crustaceans) insects centipedes starfish sea cucumbers human bird fish Know the following facts: invertebrate- animals without a backbone (snails, insects, worms) vertebrate- animals with a backbone (cats, birds, snakes, lizards) bilateral symmetry – the body structures of the animal can be divided into two sides (a left and a right side) that are alike. Most animals have bilateral symmetry. radial symmetry – the body structures of the animal equally formed around a central point asymmetry – no definite shape -Porifera (sponges) only


