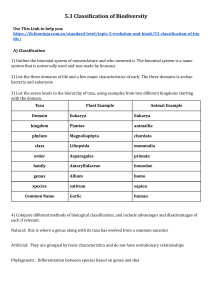
Porifera ● ● ● Asymmetrical They don't have mouth or anus because they have pores to facilitate the circulation of material Could have silica or calcium carbonate based spicules for structural support for example sea sponges Cnidaria ■ ■ ■ Obtain a radial symmetry They just have a mouth, have a single entrance body cavity Possibly have tentacles with stinging cells for capturing and disabling their prey For example jellyfish, sea anemones and coral Platyhelminthes ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Their symmetry is bilateral Have a mouth, have a single entrance body cavity Their body shape is flattened to increase SA:Vol ratio Could be parasitic Example: tapeworms and planaria Annelida ■ ■ ■ ■ Their symmetry is bilateral Have a separate mouth and anus Body consists of ringed segments with specialisation of segments Examples include earthworms and leeches Mollusca ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Their symmetry is bilateral Have a separate mouth and anus Body consists of a visceral mass, a muscular foot and a mantle Could produce shells Examples: snails, slugs, octopi, squid and bivalves Arthropoda ■ ■ ■ ■ Their symmetry is bilateral Have a separate mouth and anus Their body sections are jointed body sections and have a hard exoskeleton ( Examples include insects, crustaceans, spiders, scorpions and centipedes