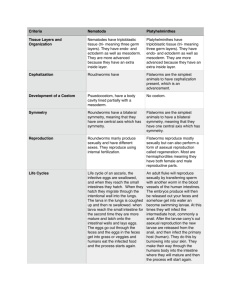
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)

The Platyhelminthes
(Flatworms)
Major Characteristics
• Animal
Characteristics
• Flattened dorsoventrally
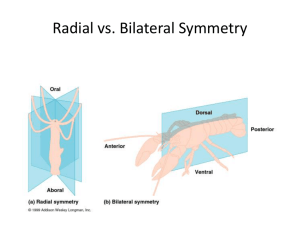
• Bilateral Symmetry
• Triploblastic
• Acoelomate
• Incomplete Gut
Body Plan: External
• Bilateral symmetry divided these organisms into distinct dorsal, ventral, anterior, and posterior portions
• Such symmetry has lead to cephalization in which the planaria have specialized senses in the anterior portion of their bodies
Body Plan: Internal
• Platyhelminthes are composed of an ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm making them triploblastic
• They contain no cavity or coelome and are thus acoelomate
Movement
• Planaria move using cilia and muscular undulations through a mucus that aids in the adhesion and traction of the cilia
• Many flatworms are parasitic and don’t move
Feeding
• Unlike most bilateral animals the mouth of the planaria is located ventrally and is incomplete (without an anus)
• They feed through a retractable pharynx and digestion occurs in a distributed digestive cavity
Reproduction
• Asexual reproduction occurs by transverse fission
• Sexual flatworms are monoecious producing both sperm and eggs
• Fertilization occurs internally and the offspring develops externally and proceeds through a larval stage