SweetChristinaHW10
advertisement

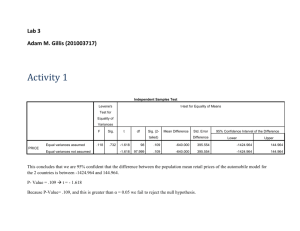
Christina Sweet 1. “Crazy t-test” ANOVA V1 Sum of Squares Between Groups df Mean Square F 1.618 1 1.618 Within Groups 957.941 61 15.704 Total 959.559 62 Sig. .103 .749 Independent Samples Test Levene's Test for Equality of Variances t-test for Equality of Means 95% Confidence Interval of the Sig. (2- F V1 Equal variances Sig. .721 t .399 df .321 tailed) Mean Difference Std. Error Difference Difference Lower Upper 61 .749 .32059 .99866 -1.67636 2.31754 .321 60.922 .749 .32059 .99757 -1.67422 2.31541 assumed Equal variances not assumed The p-values obtained from the ANOVA and t-test are the same p=.749 >.05 and therefore a significant difference was not found with either test. 2. Post Hoc Multiple Comparisons Dependent Variable:Measures 95% Confidence Interval Mean (I) Group Tukey HSD 1 2 (J) Group Difference (I-J) Std. Error Sig. Lower Bound Upper Bound 2 5.0871875* 1.6876535 .016 .692179 9.482196 3 -.8340625 1.6876535 .960 -5.229071 3.560946 4 9.0881250* 1.6876535 .000 4.693116 13.483134 1 -5.0871875* 1.6876535 .016 -9.482196 -.692179 3 -5.9212500* 1.6876535 .003 -10.316259 -1.526241 4 4.0009375 1.6876535 .088 -.394071 8.395946 3 4 Scheffe 1 2 3 4 1 .8340625 1.6876535 .960 -3.560946 5.229071 2 5.9212500* 1.6876535 .003 1.526241 10.316259 4 9.9221875* 1.6876535 .000 5.527179 14.317196 1 -9.0881250* 1.6876535 .000 -13.483134 -4.693116 2 -4.0009375 1.6876535 .088 -8.395946 .394071 3 -9.9221875* 1.6876535 .000 -14.317196 -5.527179 2 5.0871875* 1.6876535 .032 .303919 9.870456 3 -.8340625 1.6876535 .970 -5.617331 3.949206 4 9.0881250* 1.6876535 .000 4.304856 13.871394 1 -5.0871875* 1.6876535 .032 -9.870456 -.303919 3 -5.9212500* 1.6876535 .008 -10.704519 -1.137981 4 4.0009375 1.6876535 .138 -.782331 8.784206 1 .8340625 1.6876535 .970 -3.949206 5.617331 2 5.9212500* 1.6876535 .008 1.137981 10.704519 4 9.9221875* 1.6876535 .000 5.138919 14.705456 1 -9.0881250* 1.6876535 .000 -13.871394 -4.304856 2 -4.0009375 1.6876535 .138 -8.784206 .782331 3 -9.9221875* 1.6876535 .000 -14.705456 -5.138919 *. The mean difference is significant at the 0.05 level. The difference between Tukey and Scheffe is that Scheffe is more flexible and more rigorous than Tukey, but Tukey is more powerful. 3. Correlation Bank loan Correlations Years at current address Pearson Correlation Years at current Debt to income address ratio (x100) 1 Sig. (2-tailed) N Debt to income ratio (x100) Pearson Correlation -.033 .337 850 850 -.033 1 Sig. (2-tailed) .337 N 850 850 The correlation is weak and not significant sig. .,337> .05 and a -.033 person correlation is not very strong relationship. Model Summary Model 1 R .033a R Square .001 Adjusted R Std. Error of the Square Estimate .000 a. Predictors: (Constant), Years at current address 6.71975 R^2 is known as the coefficient of determination, it is the amount of variance in one dependent variable that can be explained by the independent. According to the R^2 less than 1% of the Debt to Income Ratio can be explained by Years at current Address. The amount of variance is small so years at current address does not explain a lot of the variance in Debt to Income Ratio. 5. Correlations Spearman's rho Level of education Correlation Coefficient Debt to income education ratio (x100) 1.000 .009 . .801 N 850 850 Correlation Coefficient .009 1.000 Sig. (2-tailed) .801 . N 850 850 Sig. (2-tailed) Debt to income ratio (x100) Level of I do not think there is a strong correlation between level of education and the debt income ratio, as seen with a correlation coefficient of .09, which is very weak and not even significant sig.=.801>.05.