graham
advertisement
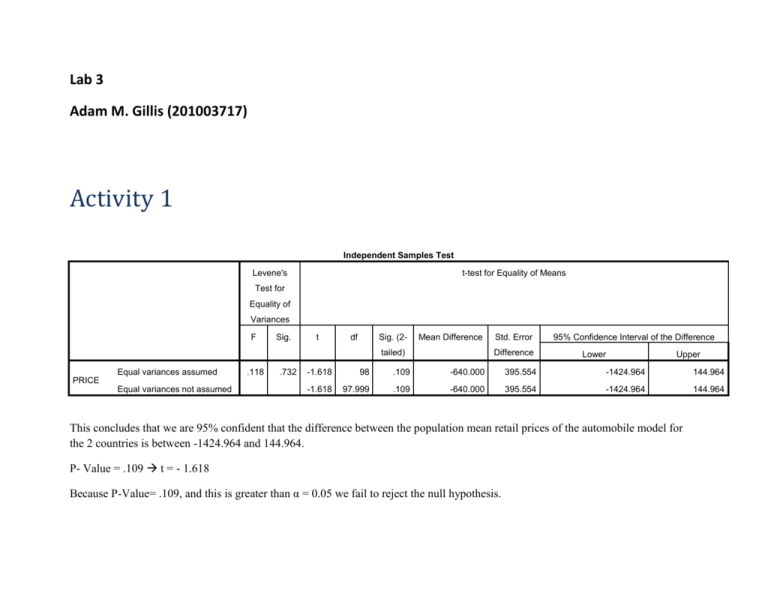
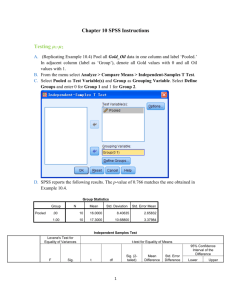
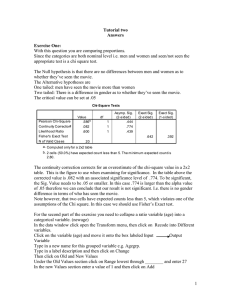
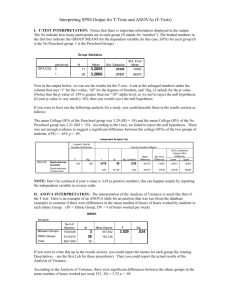
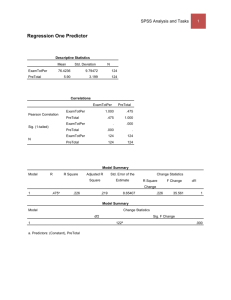
Lab 3 Adam M. Gillis (201003717) Activity 1 Independent Samples Test Levene's t-test for Equality of Means Test for Equality of Variances F Sig. t df Sig. (2- Mean Difference tailed) Equal variances assumed .118 .732 Std. Error Difference 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference Lower Upper -1.618 98 .109 -640.000 395.554 -1424.964 144.964 -1.618 97.999 .109 -640.000 395.554 -1424.964 144.964 PRICE Equal variances not assumed This concludes that we are 95% confident that the difference between the population mean retail prices of the automobile model for the 2 countries is between -1424.964 and 144.964. P- Value = .109 t = - 1.618 Because P-Value= .109, and this is greater than α = 0.05 we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Activity 2 Paired Samples Test Paired Differences Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean t df Sig. (2-tailed) 99% Confidence Interval of the Difference Lower Pair 1 MALE - FEMALE 400.000 434.613 137.437 -46.647 Upper 846.647 2.910 9 This concludes that we are 99% confident that the true mean difference between the starting salaries of males and females is between 46.647 and 846.647. P-Value = .017 t = 2.910 Because P-Value = 0.017 is greater than α = 0.01 we fail to reject the null hypothesis. .017 Activity 3 Coefficientsa Model Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized t Sig. Coefficients B (Constant) Std. Error -.100 .635 .700 .191 Beta -.157 .885 3.656 .035 1 ADVEXP_X .904 a. Dependent Variable: SALES_Y Taken from text: For every unit increase of x, the mean value of y is estimated to increase by .7 units. Therefore, for every $100 increase in advertising, the mean sales revenue is estimated to increase by $700 over the sampled range of advertising expenditures from $100 to $500.