Cell Parts and Functions Review Vocabulary: Know the words and
advertisement

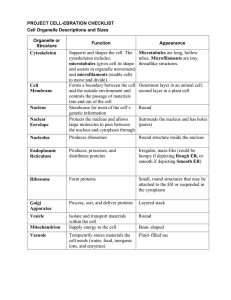
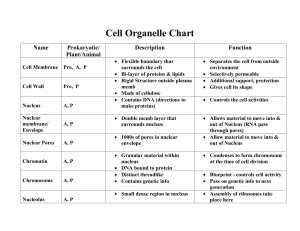
Cell Parts and Functions Review Vocabulary: Know the words and their functions Nucleus Located in the center of the cell, control center for cellular processes, DNA is housed inside of it Endoplasmic reticulum Typically attached to the nucleus or found very close to the nucleus, delivery system of the cell (can be smooth-lacking ribosomes or rough-has ribosomes attached to the surface) Golgi body Packages and ships materials through/in or out of cells Lysosome Organelle containing digestive enzymes that breaks down old cell or unneeded parts Vacuole Organelle that stores food and water. It is large and centralized in the plant cell Ribosome Small organelle where proteins are created Cell Membrane Layer that regulates what goes into or out of cells Cytoplasm Jelly-like fluid that supports the cell and suspends organelles Cytoskeleton Fibrous structures throughout the cell that are used for support Mitochondrion Organelle that breaks food parts down to release energy for other functions (that energy gets stored in ATP) Has a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. Flagella Large whip like structures on the outsides of cells that allows cells to move around Pilli Small hair like structures around the outside of the cell to help it stick to surfaces and helps in movement Cell Wall Outer most structure of plant cells that gives additional rigid support Chloroplast Organelle that is green, site of photosynthesis Eukaryote Cells that contain a true nucleus Prokaryote Cells that lack a nucleus Key Concepts: 1. List characteristics and organelles related to the appropriate type of cell Bacteria Plant Bacteria Circular DNA Cell wall Chloroplast (a few bacteria can also have) Pilli Large/central vacuole Smallest cell Flagella (some animals) Ribosome DNA Cell membrane cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondrion ER Golgi body cytoskeleton Lysosome Largest cell Animal 2. Explain the role each scientist played in the history/discovery of cells. i. Anton van Leeuwenhoek First to observe single-celled organisms and blood cells ii. Matthias Schleiden Began the cell theory iii. Rudolf Virchow Added the third part of the cell theory iv. Robert Hooke First to see and describe cells, observed cork (plant) cells, named cells 3. Explain the three parts of the cell theory. a. All organisms must be made of one or more cells b. Cells are the building blocks of all organisms c. All cells must come from existing cells 4. Why are most cells very small? What types of cells can be larger, and why? Most cells are very small because they want a larger surface area/smaller volume. This is because a large surface area (cell membrane) allows more materials to enter and leave the cell and a small volume does not require as many nutrients. As the cell grows, the surface area grows slower than the volume. Cells that can be large are most eggs. These can be large because the nutrients are already found inside of the cell. It does not matter that their surface area is small because they do not need to bring materials in. 5. Draw and label the parts of the nucleus.