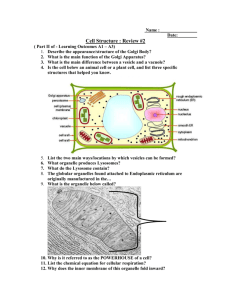
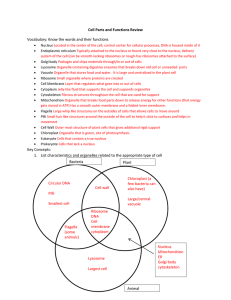
Cell Organelle Checklist: Functions, Sizes, and Descriptions
advertisement
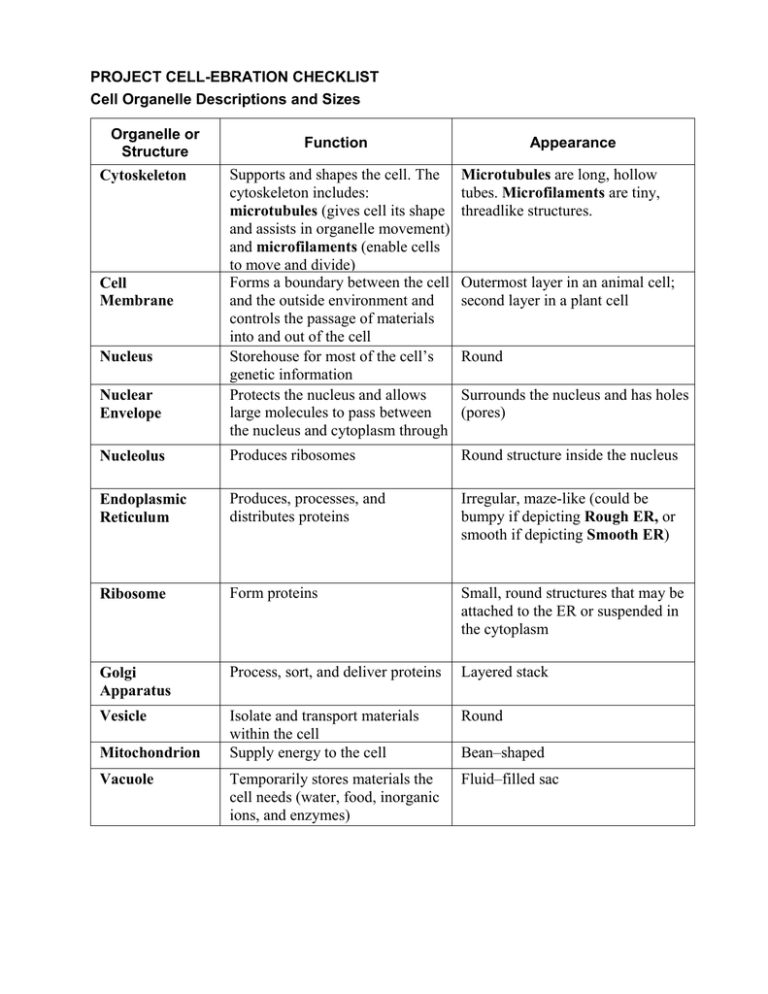
PROJECT CELL-EBRATION CHECKLIST Cell Organelle Descriptions and Sizes Organelle or Structure Function Appearance Microtubules are long, hollow tubes. Microfilaments are tiny, threadlike structures. Nucleolus Supports and shapes the cell. The cytoskeleton includes: microtubules (gives cell its shape and assists in organelle movement) and microfilaments (enable cells to move and divide) Forms a boundary between the cell and the outside environment and controls the passage of materials into and out of the cell Storehouse for most of the cell’s genetic information Protects the nucleus and allows large molecules to pass between the nucleus and cytoplasm through pores Produces ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Produces, processes, and distributes proteins Irregular, maze-like (could be bumpy if depicting Rough ER, or smooth if depicting Smooth ER) Ribosome Form proteins Small, round structures that may be attached to the ER or suspended in the cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Process, sort, and deliver proteins Layered stack Vesicle Isolate and transport materials within the cell Supply energy to the cell Round Temporarily stores materials the cell needs (water, food, inorganic ions, and enzymes) Fluid–filled sac Cytoskeleton Cell Membrane Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Mitochondrion Vacuole Outermost layer in an animal cell; second layer in a plant cell Round Surrounds the nucleus and has holes (pores) Round structure inside the nucleus Bean–shaped Organelle or Structure Function Appearance Lysosome (Animal cell) Digest and recycle foreign materials or worn–out parts Small, irregularly shaped Centriole (Animal cell) Aids in mitosis Cylinder–shaped, made of short microtubules arranged in a circle; two are present, arranged perpendicular to one another Cell Wall (Plant cell) Gives protection, support, and shape to the cell Rigid, outermost layer of a plant cell Chloroplast (Plant cell) Converts solar energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis Green, oval–shaped Approximate Sizes of Cell Organelles Organelle or Structure * Approximate Size* Microfilament 6 nm Cell membrane (thickness) 10 nm Ribosome 11 nm Cell Wall 20 nm Microtubule 25 nm Vesicle 30 nm Endoplasmic Reticulum (tube diameter) 150 nm Centriole 200 nm Lysosome 200–500 nm Golgi Body 2500 nm Nucleolus 1000 nm Mitochondrion 3000 nm Chloroplast (length) 5000 nm Nucleus 6000 nm Vacuole 4000 nm (animal) 20000 nm (plant) Size can vary greatly from one cell to another. Use only as a guide to relative size.