Movement of materials through the cell membrane
advertisement

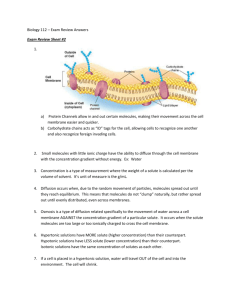
Movement of materials through the cell membrane • Passive Transport: materials move across the cell membrane by diffusion • Diffusion can cause a cell to expand or contract – Plant wilting – Red blood cell Movement of materials through the cell membrane • Osmosis- diffusion of water across a membrane • Water moves from lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration Movement of materials through the cell membrane • Active Transport: movement of materials across the cell membrane using energy from the cell -- uses transport proteins -- uses ATP Diffusion in plant cells Credit: © Jack Bostrack/Visuals Unlimited Wilted Coleus plant. Credit: © Jack Bostrack/Visuals Unlimited Coleus plant recovered from wilting. Concentration Gradient • Means the number of molecules or ions in one region is different than the number in another region • In the absence of other forces, a substance moves from a region where it is more concentrated to one where it is less concentrated: “down” gradient Diffusion • The net movement of like molecules or ions down a concentration gradient • Although molecules collide randomly, the net movement is away from the place with the most collisions (down gradient) Click to see movie oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose and other large, polar, and other small, nonpolar water-soluable molecules; ions molecules; some water (e.g., H+, Na+, K+, CA++, molecules CI–); water molecules Factors Affecting Diffusion Rate • Steepness of concentration gradient – Steeper gradient, faster diffusion • Molecular size – Smaller molecules, faster diffusion • Temperature – Higher temperature, faster diffusion • Electrical or pressure gradients Osmosis • Water molecules tend to diffuse down water concentration gradient • Total number of molecules or ions dictates concentration of water • Tonicity: relative solute concentrations Hydrostatic Pressure • Pressure that a fluid exerts against structure enclosing it • Increases with increased solute concentration • Influences the osmotic movement of water semipermeable membrane between two compartments water molecule protein molecule 2% sucrose solution distilled water 10% sucrose solution 2% sucrose solution Hypotonic Conditions Hypertonic Conditions Isotonic Conditions Hypotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution membrane permeable to water but not to solutes Red blood cell in hypertonic solution • Concentration of solute is higher outside cell • Water leaves cell Credit: © Dr. David Phillips/Visuals Unlimited Red blood cell in isotonic solution • Concentration of solute is equal inside cell and outside cell • Little movement of water from osmosis • Cell has normal shape Credit: © Dr. David Phillips/Visuals Unlimited