Cell Structure and Function
advertisement

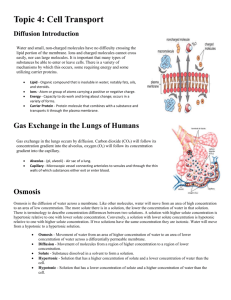
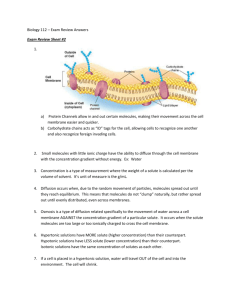
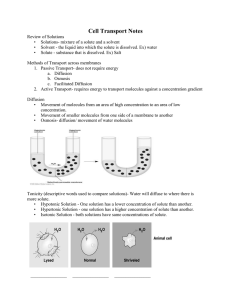
Cell Environment Lab 5 Cell Environment A water solution that contains nutrients, waste products, gases, salts, & other substances surrounds cells. External environment of the cell. Cell Environment The Plasma membrane separates the cell’s internal & external environment. Selectively permeable – small molecules can pass through freely, while larger molecules cannot. Diffusion Molecules are in constant motion due to their kinetic energy. Molecules move randomly. Random motion tends to create uniform mixtures. Net movement of molecules toward the area where they are scarce – down the concentration gradient. Diffusion allows O2, CO2, & nonpolar liquids to cross plasma membrane. Diffusion Diffusion – net movement of molecules from region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration. http://youtu.be/VY0mZUDvbH4 Osmosis Water molecules are small enough to pass through the plasma membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across the plasma membrane of a cell from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. http://youtu.be/sdiJtDRJQEc Tonicity Solutes are molecules dissolved in a solution. Tonicity – the relative concentration of solute (particles), and therefore also of solvent (water) outside the cell compared to inside the cell. Hypertonic – solution with higher solute concentration than inside the cell. Hypotonic – solution with lower solute concentration. Isotonic – solution with solute concentration equal to that inside the cell. Osmosis Movement of water into a cell creates pressure – osmotic pressure. Can cause cell to swell and burst. Cell walls protect plant cells from bursting.