Ch. 5 Guided Reading
advertisement
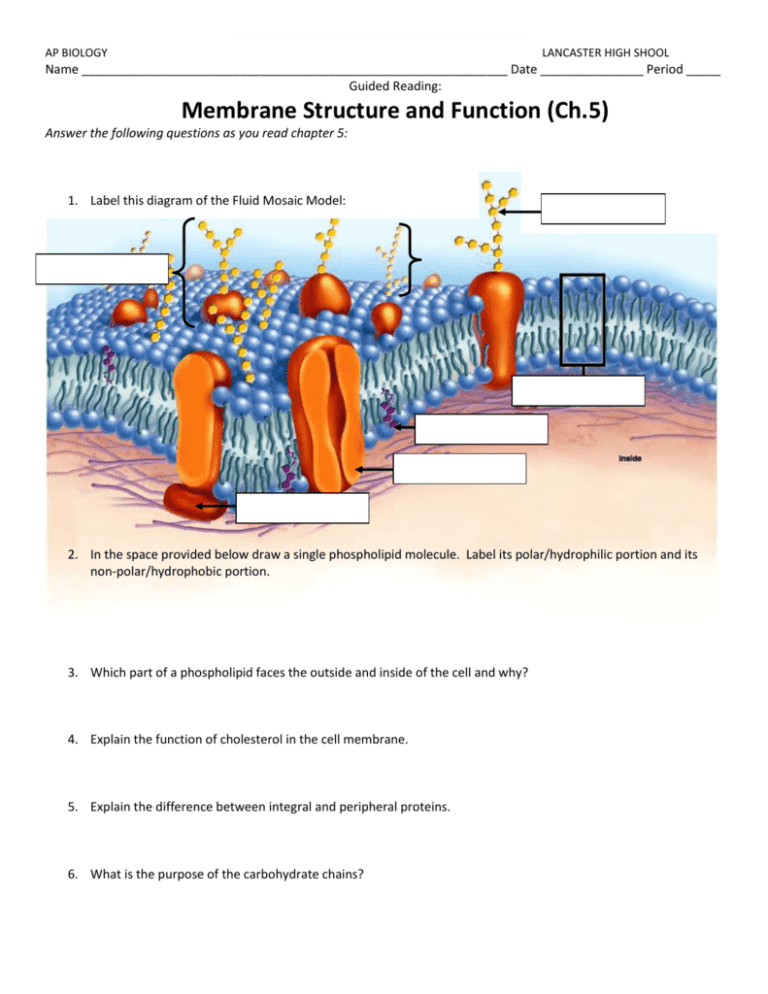
AP BIOLOGY LANCASTER HIGH SHOOL Name ______________________________________________________________ Date _______________ Period _____ Guided Reading: Membrane Structure and Function (Ch.5) Answer the following questions as you read chapter 5: 1. Label this diagram of the Fluid Mosaic Model: 2. In the space provided below draw a single phospholipid molecule. Label its polar/hydrophilic portion and its non-polar/hydrophobic portion. 3. Which part of a phospholipid faces the outside and inside of the cell and why? 4. Explain the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane. 5. Explain the difference between integral and peripheral proteins. 6. What is the purpose of the carbohydrate chains? 7. List five functions of integral proteins. 8. The cell membrane is selectively permeable. Explain what that means. Which molecules easily cross the membrane? How are molecules transported that do not easily cross the membrane? 9. What does it mean to follow a concentration gradient? 10. What is diffusion, and use this concept to explain the movement of oxygen out of the alveolus and into the bloodstream. 11. What factors can affect the rate of diffusion? 12. Osmosis is another fancy name for diffusion. But this type of diffusion is distinctly different, how? 13. What is osmotic pressure? 14. Now for the fun! Circle the correct underlined word. a. Hypotonic (hypoosmotic, solute low/high) solutions are solution in which a cell (gains/loses) water. b. Hypertonic (hyperosmotic, solute low/high) solutions are solution in which a cell (gains/loses) water. c. Isotonic shows no net ____________ 15. Let’s think about placing different cells in different solutions. a. What would happen to a freshwater unicellular organism if suddenly released into a saltwater environment? b. What would be the result on blood cells of a substitution of pure water for physiological (isotonic) saline in an IV bottle? c. Placing a plant cell in freshwater versus saltwater? d. How does a paramecium maintain osmoregulation? (you may have to look in another chapter) 16. Explain why glucose and amino acids cannot cross the plasma membrane without help from a carrier protein? 17. What two things are needed to transport molecules against their concentration gradient? 18. What does the sodium-potassium pump do? 19. Explain how macromolecules such as polypeptides, polysaccharides or polynucleotides enter and exit a cell. 20. Contrast exocytosis and endocytosis. 21. Differentiate between types of junctions in animal cells. Adhesion Tight Gap 22. What are plasmodesmata? 23. What is water pontential and explain how water is said to move? (p.467, Science Focus) 24. What are the two factors that determine water potential? (p.467, Science Focus)











