Levasseur Cell Biology Reading Guide
advertisement

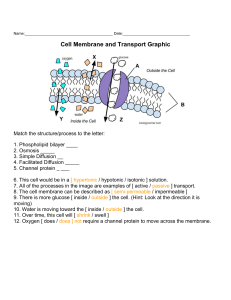
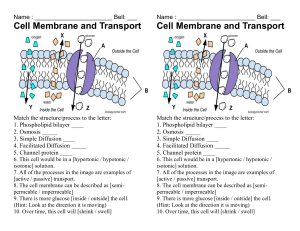
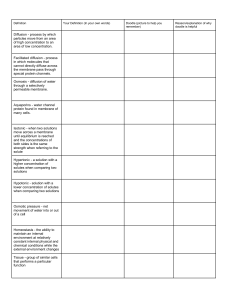
Levasseur Cell Biology Reading Guide Directions: Answer all of the questions in complete thoughts on your own paper. Section 7.1 1. 2. 3. 4. Why is staining such a useful tool when preparing a slide for the microscope? Why can’t electron microscopes be used on living specimens? How many times larger is the typical eukaryotic cell than the typical bacteria cell? What is the major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Section 7.2 5. Why is the nucleus considered the “brain” of the cell? 6. Make a table similar to the one below and fill it in. General Cellular Function Clean-up and Storage Protein Building Energy Production Create Boundaries Cell Organelles Involved 7. Make a drawing of a cell membrane and label the parts. 8. Why is a cell membrane considered to be both hydrophilic and hydrophobic? Section 7.3 9. Explain how air can enter the classroom, even when the doors are closed. What is this process called? 10. Explain how students are able to enter and exit the classroom. Give this explanation a name and compare it to a cell membrane. 11. What molecules enter cells by simple diffusion? By facilitated diffusion? 12. Draw a red blood cell in isotonic conditions. In hypertonic conditions. In hypotonic conditions. Which of the three is normal for red blood cells? 13. Why are both molecular transport and bulk transport considered “active” transport? Section 7.4 14. How do organisms made of millions of cells maintain homeostasis? 15. What do cellular junctions do? Why are they important?