Aldehydes & Ketones
advertisement

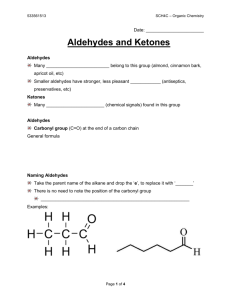
Aldehydes & Ketones Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Introduction • The aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the presence of the carbonyl group. • The carbonyl group is a functional group made up of a carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond. • Carbonyl compounds are those that contain a carbonyl group. • Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amides all are carbonyl compounds. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 2 Carbonyl Group • The carbonyl group is a functional group made up of a carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond. • Carbonyl groups are polar. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 3 Structure and Physical Properties Aldehydes • In aldehydes the carbonyl group is attached to at least one hydrogen; the second group may be attached to another hydrogen or a carbon atom. • Aldehydes are polar due to the polar nature of the carbonyl group. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 4 Structure and Physical Properties Aldehydes • Aldehydes have higher boiling points than comparable hydrocarbons, but lower boiling points than comparable alcohols. • Small aldehydes are reasonably soluble in water. • Large aldehydes are less polar and dissolve more readily in nonpolar organic solvents. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 5 Aldehydes Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 6 Structure and Physical Properties Ketones • In ketones, the carbonyl group is attached to two carbon containing groups. • Ketones are polar due to the polar nature of the carbonyl group. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 7 Structure and Physical Properties Ketones • Ketones have higher boiling points than comparable hydrocarbons, but lower boiling points than comparable alcohols. • Small ketones are reasonably soluble in water. • Large ketones are less polar and dissolve more readily in nonpolar organic solvents. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 8 Ketones Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 9 Important Aldehydes & Ketones • Many members of the aldehyde and ketone family are important as food and fragrance chemicals, medicinals, and agriculture chemicals. • Methanal (formaldehyde) is used to preserve tissue. • Ethanal causes the symptoms of hangover. • Ethanal is oxidized to produce acetic acid. • Propanone is a useful organic solvent. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 10 Preparation of Aldehydes & Ketones • Aldehydes and ketones are prepared by the oxidation of alcohols. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 11 Oxidation Reactions • Oxidation of a primary alcohol yields an aldehyde. • Oxidation of a secondary alcohol yields a ketone. • Tertiary alcohols do not react under these conditions. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 12 Oxidation Reactions • Aldehydes can be further oxidized to carboxylic acids. Ketones do not undergo further oxidation. • Tollen’s test and Benedict’s test utilize this principle to distinguish between the two. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 13 Reduction Reactions • Aldehydes and Ketones are readily reduced to alcohols by hydrogenation. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 14 Addition Reactions • The most common reaction is addition across the double bond of the carbonyl group. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 15 Aldol Condensation • Aldol condensation is a reaction in which aldehydes and ketones form larger molecules. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 16 Alcohol Abuse • According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 75,000 Americans die each year from alcohol abuse. • 35,000 die of cirrhosis of the liver. • Nearly 41,000 die of alcohol related automobile accidents. • An estimated 1400 college-age students die each year of alcohol related causes. • Alcohol abuse is the third leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 17 Antabuse • The drug tetraethylthiuram disulfide (disulfiram) is used to treat alcohol abuse. It is otherwise known as antabuse. • People who take Antabuse become violently ill after consuming any alcoholic beverage. • The compound inhibits one of the enzymes in the pathway to oxidize alcohols. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 18 Antabuse • The inhibition occurs within 1-2 hours after consuming the drug and lasts up to 14 days. • When a person who has taken Antabuse drinks an alcoholic beverage, the levels of acetylaldehyde reach levels that are 5 – 10 times higher than would normally occur after a drink. • Symptoms of a severe hangover occur within minutes and may last for hours. Dr. Michael P. Gillespie 19