Classification of Living Organisms: Domains and Kingdoms
advertisement

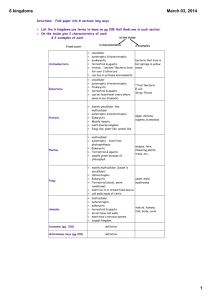
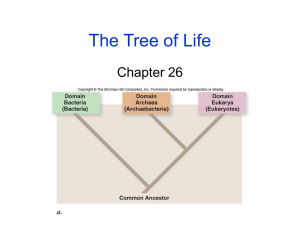
TEKS 6.12C recognize the broadest taxonomic classification of living organisms is divided into currently recognized Domains TEKS 6.12D identify the basic characteristics of organisms, including prokaryotic or eukaryotic, unicellular or multi-cellular, autotrophic or heterotrophic, and mode of reproduction, that further classify them in the currently recognized Kingdoms •What is one reason people group things into categories? •What characteristics do you think scientists look at when classifying organisms? Taxonomy is the science of classifying and naming organisms. A taxonomist is a scientist who classifies or names organisms. •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic •Sexual reproduction •Asexual reproduction •Multi-cellular •Unicellular •Autotrophic •Heterotrophic The following slides review the characteristics of each of the three domains and six kingdoms. Living organisms Prokaryotic cells Important characteristics Eukaryotic cells Domain Eukarya Domain bacteria Domain Archaea Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Eubacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Protista Kingdom Animalia Prokaryotic – lack a nucleus Unicellular – single celled Some autotrophic, some heterotrophic Reproduce asexually Some live in extreme environments ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ High salinity (salt content) Low oxygen concentrations High temperatures High or low pH Guts of grazing herbivores- produce methane Many live in oceans Prokaryotic – lack a nucleus Unicellular – single celled Some autotrophic, some heterotrophic Reproduce asexually Used in food production, oil spill cleanup, and sewage treatment plants Decomposers – break down dead organisms Some cause disease – strep throat, food poisioning, etc. http://biodidac.bio.uottawa.ca/ Eukaryotic – have a nucleus Most unicellular, some multi-cellular Some autotrophic, some heterotrophic Reproduction can be asexual or sexual Examples: amoeba, paramecium, algae, diatoms, and many more Eukaryotic – have a nucleus Some unicellular, most multi-cellular Heterotrophic Reproduction can be asexual or sexual Many are decomposers Examples: mold, mushrooms, yeast Eukaryotic – have a nucleus Multi-cellular Almost all are autotrophic Reproduce sexually and asexually Most need sunlight, water, minerals and carbon dioxide to survive Examples: trees, grasses, mosses, ferns, cactus, etc. http://biodidac.bio.uottawa.ca/ Eukaryotic – have a nucleus Multi-cellular Heterotrophic Most reproduce sexually but some asexually Examples: lizards grasshoppers, spiders, dogs, humans, worms, clams, fish, etc. An organism is eukaryotic, multicellular and heterotrophic. In which of the kingdoms would you place this organism? Fungi or animal