Classification History
advertisement

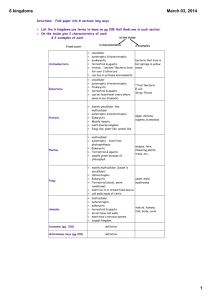
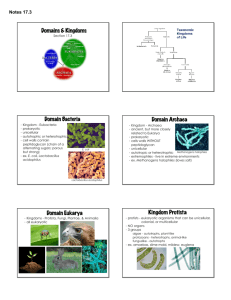
Classification History 4th century BC Aristotle- Organisms were plants or animals. Animals were placed into groups Based on where they lived. Land, air, or water. Theophrastus-Grouped plants into 3 subgroups. -tall w/one woody stem. Trees -medium w/several woody stems. Shrubs -small with nonwoody, green stems. Herbs 1700’s Linnaeus 1. Established a system of groups called TAXA. 2. Placed similar organisms into each taxon based upon structural similarities. 3. Used a hierarchy to organize taxa. The broadest taxon being Kingdom, Separated plants from animals. These Kingdoms were further split into smaller taxon until organisms were so similar they could interbreed = species. 4. Developed Binomial Nomenclature. Modern Taxonomic order of hierarchy. Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species HW: Research one organism from each Kingdom and provide its completed classification. The 6? Kingdoms Define: 1. Prokaryotic 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophic 4. Autotrophic Prokaryotic (before kernel) Cells do not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Eukaryotic (true kernel) Cells have a nucleus and membranebound organelles. Heterotrophic (other nutrition) Cannot produce its own food. Autotrophic (self nutrition) Produces its own food. Kingdom Key 1. Cell type 1a. Prokaryotic 1b. Eukaryotic Monera go to 2 go to 3 2. Environment 2a. Extreme Archaebacteria 2b. Common , true Bacteria, Eubacteria 3. # of cells 3a. Multicellular body 3b. Unicellular body 4. Mode of Nutrition 4a. Heterotorphic 4b. Autotrophic go to 4 Protista go to 5 Plantae 5. Method of Heterotrophy 5a. Absorptive Fungi 6b. Ingestive Animal HW: Create a graph representing each Kingdoms characteristics based on: a. Multicellular or Unicellular b. Cell type 1. Prokaryotic 2. Eukaryotic c. Mode of nutrition 1. Autotrophic 2. Heterotrophic d. Example pictures and/or names Kingdom Key 1. Cell type 1a. Prokaryotic 1b. Eukaryotic Monera go to 2 go to 3 2. Environment 2a. Extreme Archaebacteria 2b. Common , true Bacteria, Eubacteria 3. # of cells 3a. Multicellular body 3b. Unicellular body 4. Mode of Nutrition 4a. Heterotorphic 4b. Autotrophic go to 4 Protista go to 5 Plantae 5. Method of Heterotrophy 5a. Absorptive Fungi 6b. Ingestive Animalia Dichotomous Keys1. A list of observable traits that eventually Lead you to the name of an organism. 1a. do you understand? . . . . . Go to 2 1b. do not understand! . . . . . . Go to 1 2. Observations are presented as choices. 2a. do you want to move ahead?. .Go to 3 2b. do you want to go back? . . . Go to 1 3. Choices often split groups in half. 3a. are you a girl? . . . .Go to 4 3b. are you a boy? . . . Go to the next # 4. Each choice either directs you to a following choice or tells you the name of your organism. 4a. do you understand? . . . Dichotomous Key 4b. do not understand! . . . Go to 5 5. Example: your Kingdom Key 5a. any questions? . . . Ask me 5b. want more info? . . . Do lab p496