Classification of Organisms
advertisement

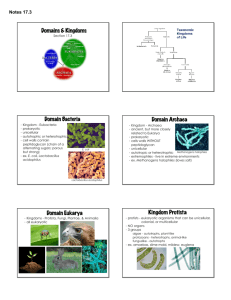
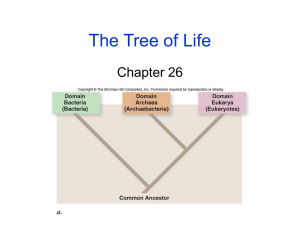
Classification of Organisms Biology Chapter 17 Classifying Organisms • Taxonomy: the science of describing, naming, and classifying organisms – Taxon: a group within a taxonomic system • Aristotle: classified organisms into two groups – Plants and animals • Why isn’t this useful? Carolus Linnaeus • Devised system of grouping organisms into hierarchical categories – Using form and structure • • • • • • • • Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Binomial Nomenclature • Two part naming system (scientific name) – Use genus and species name – Written in italics with genus name capitalized – In Latin because it is an unspoken language, so it never changes – Example • Humans: Homo sapiens Systematics • Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species – Phylogenetic Diagram (phylogenetic tree) • Looks like a family tree and has branching pattern that indicates how closely related subset taxa are thought to be Cladistics • Cladistics – A system the uses shared characteristics and derived characters as the only criteria for grouping • Shared character: a feature that all members in the group have in common • Derived character: a feature that evolved only within the group under consideration Cladistics • Clad: used to describe a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all of its descendants • Cladogram: Diagram • Molecular Cladistics: looks at derived amino acids at each position in a protein Three Domains of Life • Domain Bacteria – Prokaryotic – Single-celled – Have a cell wall – Heterotrophic and autotrophic – Ex: bacteria Three Domains of Life • Domain Archaea – Prokaryotic – Most live in harsh environments – Have cell walls – Unicellular – Heterotrophic and autotrophic Three Domains of Life • Domain Eukarya – Have eukaryotic cells – Includes kingdoms plants, animals, fungi, and protists Domain Eukarya • Kingdom Protista – Eukaryotic – Not plants, animals or fungi – Most are unicellular – Some multicellular but lack tissue organization – Autotrophic or heterotrophic Domain Eukarya • Kingdom Fungi – Eukaryotic – Heterotrophic – Unicellular and multicellular – Absorb their food through extracellular digestion Domain Eukarya • Kingdom Plantae – Eukaryotic – Muclticellular – Most are autorophic Domain Eukarya • Kingdom Animalia – Eukaryotic – Multicellular – Heterotrophic – Develop from embryos