6 kingdoms
advertisement

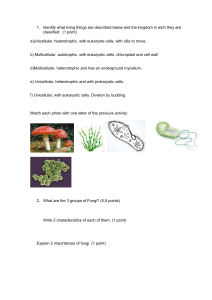
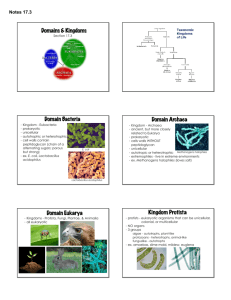
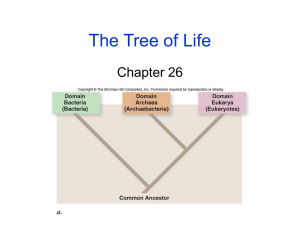
6 kingdoms March 03, 2014 Directions: Fold paper into 8 sections long ways • List the 6 kingdoms use terms to know on pg 208 Holt Book,one in each section. • On the inside give 2 characteristics of each on the inside & 2 examples of each 2 characteristics Front cover Archaebacteria • • • • • unicellular autotrophic & heterotrophic prokaryotic terrestrial & aquatic Archae - "ancient" Bacteria lived for over 3 billion yrs can live in extreme environments bacteria that lives in hot springs in yellow stone • • • • • unicellular autotrophic & heterotrophic Prokaryotic terrestrial & aquatic can be found most every where (even in our stomach) "True" Bacteria E-coli Strep Throat • mostly unicellular, few multicellular autotrophic & heterotrophic Eukaryotic Mostly Aquatic most diverse kingdom fungi-like, plant-like, animal-like algae, diatoms, euglena, & amoebas • Eubacteria Protista • • • • • • • Plantae • • • • Fungi Animalia 2 examples multicellular autotrophic - food from photosynthesis Eukaryotic Terrestrial & aquatic usually green because of chlorophyll mosses, fern, flowering plants, trees, etc... • • mostly multicellular, (yeast is unicellular) Heterotrophic yeast, mold, Eukaryotic mushrooms Terrestrial (moist, warm conditions) must live in or around food source cell walls made of chitin • • • • • • • multicellular heterotrophic eukaryotic terrestrial & aquatic do not have cell walls most have a nervous system largest kingdom • • • taxonomy (pg. 202) definition dichotomous keys (pg.202) definition insects, humans, fish, birds, coral 1