NOTES FOR CLASSIFICATION 1) Aristotle was the first person to

NOTES FOR CLASSIFICATION
1) Aristotle was the first person to classify organisms.
2) Aristotle classified all organisms into two groups
Plants & Animals
Taxonomy-science of classifying organisms
A.
Linnaean System
1.
Carolus Linnaeus ( 1700s) developed bionomial nomenclature
2.
Language
3.
Binomial Nomenclature
Ex. Genus-Species
B.
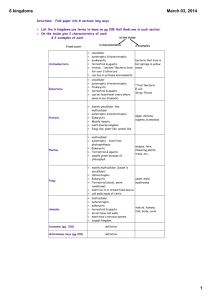
Order of classification groups
D-omain (Eukaryote)
K-ingdom (Animalia)
P-hylum (Chordata)
C-lass (Mammalia)
O-rder (Primates)
F-amily (Hominidae)
G-enus (Homo)
S-pecies (Sapiens)
Example of Binominal Nomenclature
Genus Species
Homo sapiens
Classification & Identification
Morphology- physical appearance
Embryology- appearance of embryos
Chromosomes-
Biochemistry-
Some Models used in classification
Phylogeny: Evolutionary history of a species
Phylogenetic tree: Model of inferred relationship among organisms
Biosystematics: A form of taxonomy that examines reproduction and gene flow
Dichotomous key:
A written set of choices that leads to the name of an organism
Why do we classify organisms?
So we can organize them to make them easier to study
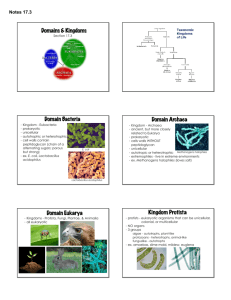
Countinously changing as we learn more and with the addition of molecular biology– use to be only plants and animals, then went to 3 kingdoms (plants, animals and monera) , then 5 Kingdoms and later 6 Kingdoms
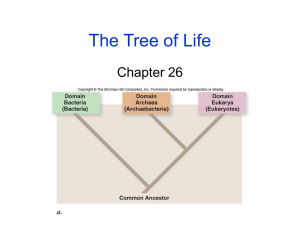
3 Domains
Three Domains
1) Bacteria (Eubacteria)
2) Archaea
3) Eukaryotes
Archaebacteria
1) Prokaryotic Cells
2) Autotrophic or heterotrophic
3) Usually found in extreme environments.
4) Most Unicellular
5) Example - thermoacidophiles
Eubacteria
1) Prokaryotic Cells
2) Autotrophic or heterotrophic
3) Most unicellular
4) Example - cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)
Domain Eukaryote
1) Contains the kingdom that are Eukaryotes
2) Plant
3) Animal
4) Protists
5) Fungi
Kingdom Protista
1) Eukaryotic cells
2) Autotrophic or heterotrophic
3) Unicellular/multicellular
4) Example - Ameba, paramecium
Kingdom Fungi
1) Eukaryotic cells
2) Heterotrophic
3) Multicellular
4) Examples: mushrooms/yeast
Kingdom Plantae
1) Eukaryotic cells
2) Autotrophic
3) Multicellular
4) Example-poison ivy
Kingdom Animalia
1) Eukaryotic cells
2) Heterotrophic
3) Multicellular
4) Example - humans