VSEPR Theory: Molecular Geometry & Polarity Worksheet
advertisement
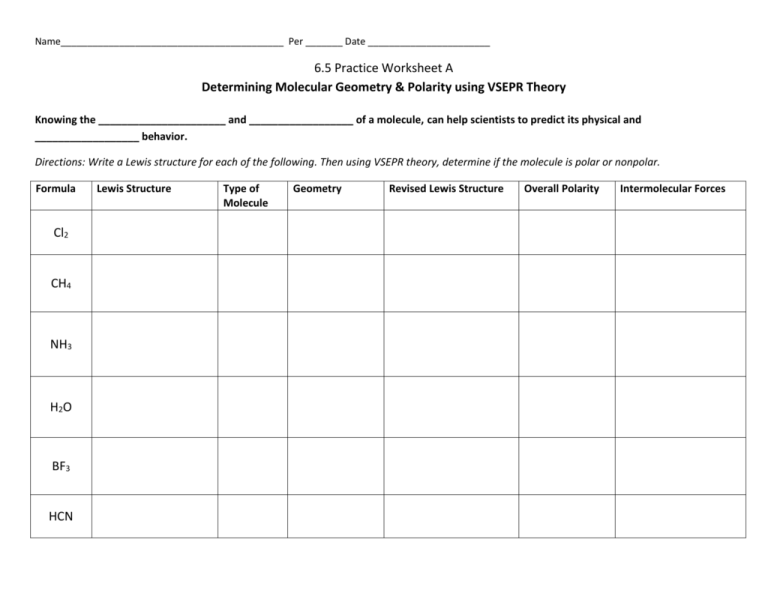
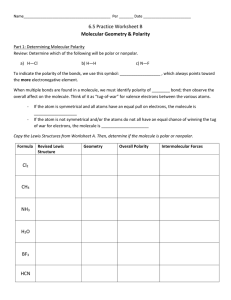
Name__________________________________________ Per _______ Date _______________________ 6.5 Practice Worksheet A Determining Molecular Geometry & Polarity using VSEPR Theory Knowing the ______________________ and __________________ of a molecule, can help scientists to predict its physical and __________________ behavior. Directions: Write a Lewis structure for each of the following. Then using VSEPR theory, determine if the molecule is polar or nonpolar. Formula Cl2 CH4 NH3 H2O BF3 HCN Lewis Structure Type of Molecule Geometry Revised Lewis Structure Overall Polarity Intermolecular Forces How do we predict the geometry and polarity of a molecule using VSEPR theory? 1. Draw a Lewis structure for the molecule. VSEPR theory states: if any lone pairs of electrons are found on the __________ atom, these electrons decrease the bond angles of atoms attached to it. What are lone pairs? 2. Draw a revised Lewis structure to show a more accurate picture of how lone pairs (or a lack of lone pairs) have affected the shape of the molecule. 3. To indicate the polarity of the bonds, we use this symbol: __________________ , which always points toward the more electronegative element. Electronegativity 4. When multiple bonds are found in a molecule, we must identify polarity of ________ bond. 5. Observe the overall polarity of the molecule. Think of it as “tug-of-war” for valence electrons between the various atoms. - ______________ molecules: If the atom is symmetrical and all atoms have an equal pull on electrons - ___________________ molecules: If the atom is not symmetrical and/or the atoms do not all have an equal chance of winning the tug of war for electrons Summary of Bond Polarity: - Bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules are always _______________________ . - Linear, trigonal planar, and tetrahedral are often ____________________, but can be ____________________, if all the atoms attached to the center are not the same.