Molecular Models Lab
advertisement

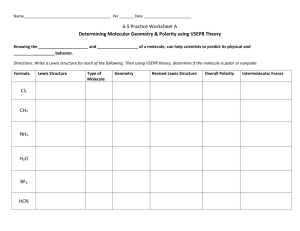
Accel Chem Covalent Bonding Name: Molecular Models Lab Covalent bonding occurs when atoms share valence electrons. In the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory, the way in which valence electrons of bonding atoms are positioned is the basis for predicting a molecule’s shape. This method of visualizing shape is also based on the molecule’s Lewis structure. Guiding Question: How do the Lewis structure and positions of valence electrons affect the shape and polarity of a covalent molecule? Materials: Molecular Model Kit Procedure: 1. Obtain a molecular model kit and write down the color code of atoms: H: O: C: Cl: S: N: Note the different sized-connecters that you will use. Short connector = single bond. Long connecter = double and triple bonds. Lone pairs of electrons are assumed on the models, but they should be drawn in your Lewis structures. 2. Construct each of the following molecules. Complete the table by writing the formula, structural diagram, shape, polarity of the bonds, and polarity of the molecule. You may use your textbook or reference sheets for additional help. Cl2; O2; N2; H2O; CO2; NH3; CCl4; CH2Cl2; SO3; HCN; CO; 3 additional examples of your own choosing. Analysis and conclusion: Each person will respond to the following questions in pen (or typed) on a separate piece of paper, and it is due on _______________. You will also attach your data table. These are questions and reflections that pull many pieces from chemistry together and need to reflect your best thinking. 1. Based on the molecular models you built and observed in this lab, rank single, double, and triple bonds in order of increasing flexibility and in order of increasing strength. Accel Chem Covalent Bonding Name: 2. What is meant by polar and nonpolar? Describe the difference thoroughly using the term “electronegativity.” 3. What is VSEPR? How does it help us determine the shape of a molecule? 4. Explain why H2O and CO2 molecules have different shapes. Explain how their different shapes affect the different polarities of the molecules. 5. Explain why methane (CH4) and dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) would have the same shape but different polarities. 6. How do lone pairs of electrons on the central atom affect the polarity and shape of a molecule? 7. One of the molecules from this lab undergoes resonance. Identify the molecule that has three resonance structures, draw the structures, and explain why resonance occurs. 8. Look up additional information on Gilbert Lewis, the person whom Lewis structures are named after. He led an interesting life, but unfortunately was never awarded the Nobel Prize for his achievements. Write a couple paragraphs about his work and scientific achievements. Cite your sources (www.google.com is not a source). The internet is not the only place you can look…try a book! Accel Chem Covalent Bonding Formula Lewis Dot Structure Name: VSEPR Shape Are the bonds Is the molecule polar/nonpolar? polar/nonpolar?