6.5 Practice Worksheet B: Polarity and Intermolecular Forces
advertisement

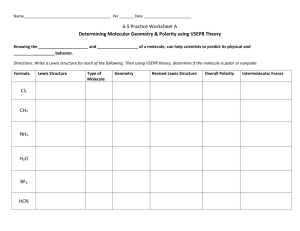
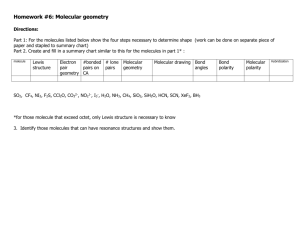
Name__________________________________________ Per _______ Date _______________________ 6.5 Practice Worksheet B Molecular Geometry & Polarity Part 1: Determining Molecular Polarity Review: Determine which of the following will be polar or nonpolar. a) H—Cl b) H—H c) N—F To indicate the polarity of the bonds, we use this symbol: __________________ , which always points toward the more electronegative element. When multiple bonds are found in a molecule, we must identify polarity of ________ bond; then observe the overall affect on the molecule. Think of it as “tug-of-war” for valence electrons between the various atoms. - If the atom is symmetrical and all atoms have an equal pull on electrons, the molecule is ___________________ If the atom is not symmetrical and/or the atoms do not all have an equal chance of winning the tug of war for electrons, the molecule is _____________________ Copy the Lewis Structures from Worksheet A. Then, determine if the molecule is polar or nonpolar. Formula Cl2 CH4 NH3 H2O BF3 HCN Revised Lewis Structure Geometry Overall Polarity Intermolecular Forces Summary of Bond Polarity: - Bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules are always _______________________ . - Linear, trigonal planar, and tetrahedral are often ____________________, but can be ____________________, if all the atoms attached to the center are not the same. Part 2: Intermolecular Forces (IM forces) Once the molecular geometry and polarity of a molecule is determined, we can use this information to indicate the type of ____________________ forces which are present that will affect the molecules chemical and physical behavior. Remember: Intermolecular forces refer to the attraction ________________ molecules. This is just like the “internet,” which is the network that links millions of computers together. o These always weaker than the forces hold an individual molecule together (intramolecular forces) i.e. covalent, ionic, or metallic forces. What property is often used to investigate the strength of intermolecular forces present in a sample? List the four types of intermolecular forces, beginning with the weakest: When is this possible? ______________________________ : this occurs to some degree in all molecules! ______________________________ : ______________________________ : ______________________________ : Now that you know this information, go back and fill in the intermolecular attractions for the molecules above. Part 3: Extra Examples Write the Lewis Structure, state the general formula, geometry, polarity and any intermolecular forces! A) CO2 B) CH3Cl