Biochemistry Review Guide 2014
advertisement
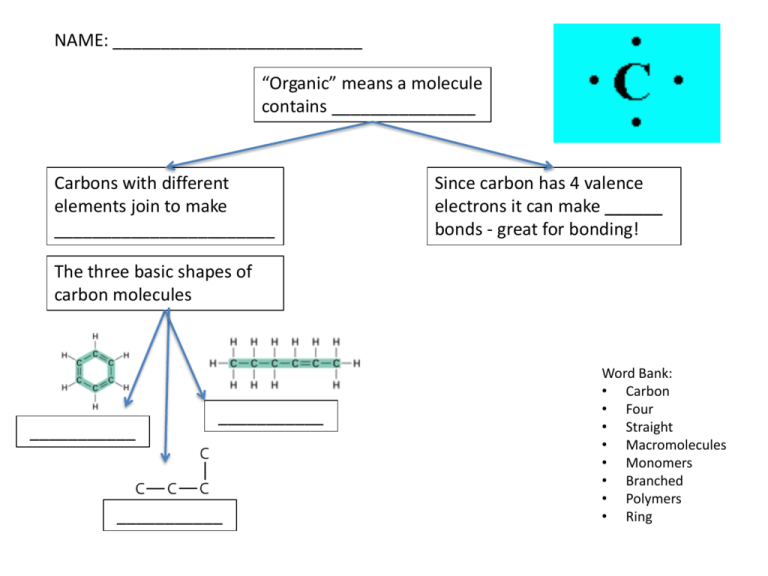
NAME: __________________________ “Organic” means a molecule contains _______________ Carbons with different elements join to make _______________________ Since carbon has 4 valence electrons it can make ______ bonds - great for bonding! The three basic shapes of carbon molecules ___________ ___________ ___________ Word Bank: • Carbon • Four • Straight • Macromolecules • Monomers • Branched • Polymers • Ring Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation Reaction) Is how larger molecules are by So bonds can be made between To build up for example Hydrolysis Is how larger molecules are by • • • • • • • • So bonds in Are broken down into For example Removing water Polymers Monomers Adding water Built up Broken down Starch glucose+ glucose+ glucose Glucose + fructose sucrose. Carbohydrates Foods Used for Different levels of complexity Means 1 sugar Means 2 sugars examples v examples examples v v v Found in insect/lobster chitin Short term energy storage Fructose v Found in plants for v Glycogen • Sugar • Starch Sucrose • Glucose storage v v v • • • • • Means many sugar Found in plants for Found in animals for v • • • • Glucose Lactose Pasta Glucose storage • • • • v Structure Energy Galactose Fruit • • • • Cellulose Disaccharide Cell wall Polysaccharide v • • • • Exoskeleton Monosaccharide Milk Maltose foods Are used for Lipids 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. All lipids are (Which means they do not mix with water) 3 groups or classes of lipids are v Made of v and Goes towards the inside away from water v Which can be v v Solid at room temp, and contains Liquid at room temp and contains v v Examples v v v v have 4 fused rings and makes up Used for v Hormones Examples v Goes towards the outside toward water Component of v v v v If there is too much it can lead to v Lipid word bank: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Oils Triglyceride Hydrophobic Steroids Cholesterol Insulation Cell membranes Protection Testosterone Unsaturated Butter Waxes Fatty acids Estrogen Saturated Long term energy storage Hormones Component of cell membrane fats • • • • • • • • • • • • Avocado Phospholipids Bilayer Glycerol No double bonds between the carbons Cardiovascular Disease ( Heart Disease) Hydrophobic Tails At least one double bond between the carbons Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Nuts Boundary that surrounds cells Foods Shape of protein determines Proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. Used for Made up of When the shape changes it is called 1. 2. 3. Which can be caused by Which have the following chemical structure(draw) Build up by forming Organized into 4 levels of structure 1° The “R” group is the variable side group v To form a protein which is also known as 2° 3° 4° 1. 2. Word bank for proteins: • Peptide bonds • polypeptide • 20 amino acids • Proteins • Meat • Hormones (chemical signals) • Denature • Folding of amino acids (alpha helix and beta sheets) • pH • Folding into 3D structure to get function • Structure (hair and nails) • Dairy • Eggs • Beans • More than one polypeptide chain • Function • Temperature • Enzymes • Order of amino acids • Determines how the protein will fold Test for Organic Molecules Use indicators To Test for Mixed with Mixed with + Positive results Mixed with Positive results Negative results Positive results On paper it will Negative results Negative results Word Bank • Biuret Solution • Heat for 5 min • Orange • Proteins • Stain red • Make it look waxy • Purple • brown • • • • • • Blue Benedict’s Solution Starch Simple monosaccharaides Iodine Blue/black • • • • • Lipids Sudan IV Black Light orange Carbohydrates Enzymes Are made of Effected by It works by They function as What the enzyme binds Causes In binds in the area called the To Leads to • • • • • Active site • Denaturation Loss of function • Reduce activation energy Protein Temperature substrate • • • pH Catalyst Speed up a reaction