Structure and function of macromolecules
advertisement

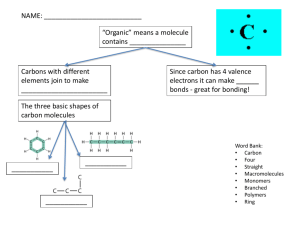
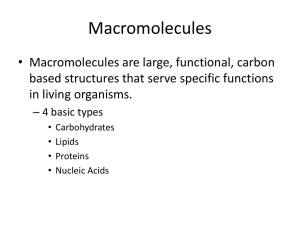
Structure and function of macromolecules B Assignment! • We will make a foldable with the following information • you will need • scissors • 3 pieces of paper • to listen for each cut and fold What are macromolecules? • Macromolecules are large organic (contain carbon living or once living organisms) molecules • aka polymers • made of smaller building blocks called monomers What makes carbon important? • 4 electrons in its outer shell • outer shell is capable of holding 8 • carbon is capable of making up to 4 bonds with other atoms • forms covalent bonds with other atoms (very strong) • usually shares with C, N,O, or H • ratio is 1:2:1 • ex. glucose = C6H12O6 How are macromolecules formed and broken down? • Dehydration synthesis = makes macromolecules by pulling out a water molecule • hydrolysis = takes macromolecules apart by adding a water molecule What are carbohydrates? • carbohydrate = sugars, organic molecules containing: • carbon • hydrogen • oxygen 1:2:1 ratio • 4 types: • • • • simple sugars starch cellulose glycogen • monomer = simple sugars, monosaccharides What types of sugars are there? • monosaccharides • simple sugars • glucose • fructose • galactose • disaccharides • 2 attached sugar molecules • sucrose (glucose + fructose) • maltose (glucose + glucose) • lactose (glucose + galactose) • polysaccharides • many attached sugars • starch • cellulose • glycogen Why are saccharides useful to organisms? • glucose – major energy source provided by plants • photosynthesis • starch – storage of glucose in plants • cellulose – makes cell walls of plants • glycogen – storage of glucose in animals How can carbs be tested for? • benedicts solution – tests for simple sugars • put benedicts solution into suspect sugar solution • boil • look for color change blue orange/green/ red • Lugols solution (IKI) – test for starch • put into suspected starch solution • look for color change brown black/purple What are lipids? • fats • saturated fats • unsaturated fats • transfats • not soluble in water (don’t dissolve) • storage for more energy • • • • fats oils phospholipids (which make up?) triglycerides What are the types of fats? • saturated • animal fat • solid at room temperature • no double bonds • C chain saturated with single H bonds • unsaturated • plant fat • liquid at room temperature • carbon chain with at least 1 double bond • Triglycerides • glycerol with 3 fatty acid chains • E shape What are lipids used for? • long term energy storage • insulate and waterproof the organism • chemical messages • protect against physical shock How can lipids be tested for? • spot test • rub suspected lipid on brown paper • look for shiny spot What are proteins? • Also called polypeptides • made of C,H,O,N, and Sulfur in some cases • monomer: 20 different amino acids • bonded together with peptide bonds • 8 essential amino acids only obtained from food How are proteins structured? • primary • amino acids in straight chains made of peptide bonds • secondary • 3D structure • folded coils or sheets • H bonds • Tertiary • called subunits • secondary structures bent and folded into globular shape • quaternary • • • • 2 or more subunits globular shape form in water make enzymes What are proteins used for? • catalyst – enzymes control reaction rates • storage – small molecules can attach to proteins • transport – channel proteins in the cell membrane • messenger – hormones • antibodies – bind to pathogens • regulation – help maintain homeostasis • structure – provide support How are proteins detected? • biuret solution • place suspected protein solution into biuret solution • look for color change from blue purple What are nucleic acids? • made of chains of nucleotides • linked by dehydration synthesis • 2 types • DNA • RNA What are nucleotides? • Made of a: • phosphate group • pentose sugar (5 carbons) • 5 different nucleotides • • • • • adenine thymine cytosine guanine uracil What are the differences in DNA and RNA • DNA • double stranded • 4 bases • • • • A C T G • RNA • Single stranded • 4 bases • • • • A C U G What are enzymes? • -ase = enzyme • examples of enzymes • • • • carbonic anhydrose – keeps carbon dioxide from building in blood lipase – speeds digestion of lipids RNA polymerase – speeds up transcription of RNA Catalase – breaks down alcohol http://www.pinterest.com/zeldabean3/biology -jokes/ Assignment! • Testing for macromolecules • Virtual lab • Hands on lab