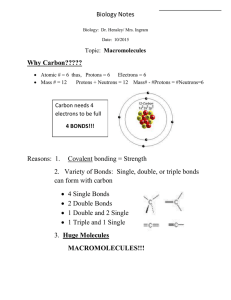
CARBOHYDRATES
advertisement
Macromolecules CARBOHYDRATES • contain C,H,O usually ratio 1C: 2 H : 1 O • • • • large chains & rings of C w/diff. molecules 2-3% of body wt. are sugars or starches provide most of the energy used by cells • If not immediately needed for ATP synthesis, they are converted into glycogen or fat Monosaccharides • simple sugar : single chain or single ring (3-7 carbons) • Building blocks (monomers) of carbohydrates – Glucose: main energy source for cells – Fructose: found in fruits, sweetest – Galactose: found in milk – Ribose, Deoxyribose: make up DNA, RNA Isomers • are compounds with the same chemical formula but different structural formulas Disaccharides • Double sugar –Maltose: malt sugar (glucose + glucose) –Sucrose:cane sugar (glucose + fructose) –Lactose: milk (glucose + galactose) Form by: DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS • Removal of water to join 2 monomers • Forms dimers, polymers Polysaccharides • complex molecules composed of three or more monosaccharides • Ideal for storage • Lack sweetness of mono + disaccharides • Glycogen: storage in animals –Muscles, liver • Starch: storage molecule for plant • Cellulose: gives strength and rigitiy to stalks and stems (Potatoes, carrots, etc) STARCH GLYCOGEN LIPIDS- large nonpolar organic molecules •18%-25% of body weight •fewer covalent bonds •fat-marbled meats, egg yolks, milk, oils, waxes •Most lipids are insoluble in water but dissolve in other lipids and alcohol, acetone Fatty Acids -unbranched C chains that make up most lipids • long carbon chains with a carboxyl group at the end (COOH) • carboxyl end is polar and thus hydrophilic-attracted to water • hydrocarbon end is non-polar and thus hydrophobic- water fearing • Saturated fatty acid-a fatty acid where all the carbon to carbon bonds are single bonds • Unsaturated fatty acid- there is at least on carbon to carbon double bond • Higher ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms – causes them to have more carbon to hydrogen bonds which store more energy….hence fats having a higher caloric value NEUTRAL FATS (TRIGLYCERIDES) • BUILDING BLOCKS – 3 Fatty acids – Glycerol • most common in the body • Concentrated sources of energy • adipose tissue insulates and protects organs • SOLID: (animal fats) –Saturated: carbons have single bonds • LIQUID: (plant oils) –Unsaturated: carbons have double or triple bonds PHOSPOLIPIDS • Important in cell membranes – allows them to be selective • POLAR HEAD – attracts and interacts with water and ions (hydrophilic) • NONPOLAR TAILS- ‘hydrophobic’ STEROIDS • Four interlocking rings • Structure differs from other fats • Made largely of H and C atoms CHOLESTEROL – is most important molecule in steroids – meat, eggs, cheese – Certain amount made in liver – Found in ALL cell membranes • Provide rigidity • Facilitates communication between cells – Particularly abundant in brain – Used to form sex hormones, cortisol (stress hormone), bile salts, and vitamin D ATHEROSCLEROSIS deposit of FAT in artery walls ATERIOSCLEROSIS hardening of arteries HOW DO WE MAINTAIN HOMEOSTATIS? ‘POLLY’ UNSATURATED OLIVE ‘OYL’ • Omega-3 Fats (Fish, walnuts) • safflower, corn, sunflower and soybean oils PROTEINS • complex in structure • composed of amino acids • larger range of functions than carbohydrates and lipids • normal lean adult is 12 -18% proteins PROTEIN STRUCTURE FUNCTIONS • Structural – collagen fibers in connective tissues – keratin is in hair and skin STRAIGHT HAIR CURLY HAIR Healthy Cuticle Damaged Cuticle ANDROGENIC ALOPECIA • 50 and 80% of Caucasian men • Asian males have lower incidences • present in the general female population at a rate between 20 to 40% Regulatory • hormones • help regulate growth and development • insulin - regulates blood sugar levels • guide neuron growth DIABETES • Types 1 or 2 (more common) • Not enough insulin or cells ignore insulin (high blood glucose level) Contractile actin and myosin filaments found in muscle cells Contractile aid in cell division, movement and sperm propulsion Immunological antibodies • bind with and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and viruses • function in immune response • help protect body from foreign substances AIDS Transport • hemoglobin carries oxygen and carbon dioxide, lipoproteins carry lipids • iron transport Sickle Cell Anemia Catalytic • essential to almost every biochemical reaction in the body • increase rate of chemical reactions