Quality Improvement: Problem Solving
advertisement

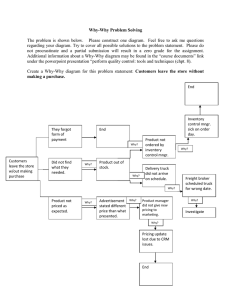
Agenda Review Homework • Problems: Ch 2: 3, 7, 12 Lecture/discussion • Chapter 3: Problem Solving • Week 6 Assignment • • PDSA • • • • • Week 5 Deming Text-10 Point Method Florida Power and Light Xerox HP • Homework • Problems Ch 3: 2, 4 Desksides: 7 QC Tools • Flow chart • Pareto chart • Histogram • Cause and Effect Diagram • Check sheet • Scatter diagram • Control chart Management tools • Why-why • Force field analysis • Brainstorming* Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Chapter Three Quality Improvement: Problem Solving What is QC Problem Solving? “Problem solving, the isolation and analysis of a problem and the development of a permanent solution, is an integral part of the qualityimprovement process”. • • Not hit or miss, but objective and systematic Not directed at symptoms, but rather at root causes Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Problem Solving Process Symptom Recognition Fact Finding Problem Identification Follow Up Idea Generation Solution Development Plan Implementation Quality Improvement: Problem Solving All Managers Need Problem Solving Skills 80% of problems are external to QC organizations Quality problems transcend individual functions Companies need multi-discipline problem solving approach Management involvement and commitment is crucial Source: Feigenbaum, Total Quality Control, 1991, p. 151. Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Problem Solving Skills for Managers Understand and utilize a systematic problem solving process Ask the right questions Present information clearly and unambiguously Make judgments based on information PDSA Cycle Seven QC Tools Quality Improvement: Problem Solving 10 Problem Solving Steps Recognize Problem ACT PLAN STUDY DO Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Gap Analysis Internal or External Supplier Input Process A Output Internal or External Customer Requirements and Expectations Quality Characteristics Are there any gaps? Quality Improvement: Problem Solving 10 Problem Solving Steps Continuous improvement Ensure performance ACT Evaluate Solution STUDY DO Implement Solution Recognize Problem Form quality improvement teams Define Problem Analyze PLAN Problem Determine Possible Causes Identify Possible Solutions Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Florida Power & Light’s 7 step model Identify a problem area Identify the problem’s component parts Search data for root causes Identify and select countermeasures Confirm the problem responds to the correction Assure non-recurrence Decide what will be done with future problems - evaluate team effectiveness Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Xerox Problem Solving Process Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Process Analysis Method UNDERSTAND SELECT ANALYZE ADOPT PLAN CHECK DO Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Why do we need the 7 QC tools? TQM is data driven: data are impersonal; opinions are not. Experience is gained quickest by collecting and analyzing data. The 7 QC tools provide common methods of analysis to help problem solving teams operate effectively. Quality Improvement: Problem Solving PDSA and QC Tools Brainstorming Pareto analysis ACT Run charts Control charts Histograms Check sheets STUDY Scatter diagrams Pareto charts Why-Why diagram PLAN DO Cause and effect diagram Scatter diagrams Control charts Check sheets Run charts Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Brainstorming Purpose - generate a list of • • • problems opportunities ideas Success requires • • • • no criticism no arguing no negativism no evaluation Quality Improvement: Problem Solving Problems for “Why-Why” discussion What are the root causes? • • • 787’s not being delivered on time Utility outages too frequent Fast food outlet profits falling Construct a “Whywhy” diagram • • List problem statement Ask why 5 times; record responses Quality Improvement: Problem Solving