diseases that cannot be spread from person to person Pathogens
advertisement

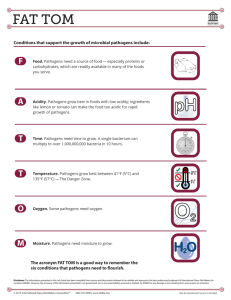
Vocabulary Antigen: any substance release by Disease: any condition that interferes with the proper functioning of the body Communicable: disease that can be passed to a person from another person Noncommunicable: diseases that cannot be spread from person to person Pathogens: disease-causing organisms that are so small they can only be seen through a microscope Infection: a condition that occurs when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and cause harm Immune System: combination of body defenses made up of cells, tissues, and organs that fight off pathogens and disease. Immunity: your body’s ability to resist the germs that cause a particular disease. invading pathogens Antibodies: proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body. Vaccine: preparation of dead or weakened pathogens that causes the immune system to produce antibodies. Antibiotics: medicines that reduce or kill harmful bacteria in the body. Communicable vs Noncommunicable Communicable can be passed person to person, noncommunicable can’t. Communicable diseases can be from bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens. Disease Prevention Communicable disease can be prevented by avoiding the bacteria. This includes bactyeria and other pathogens in our food, water, and environment. We can also wash our hands and boost our immune system to help fight off diseases. Noncommunicable diseases can be prevented through our lifestyle. Habits including refraining from drug use, eating healthy, and exercise help us prevent noncommunicable diseases. Types of Pathogens Many types of pathogens, but we focused on 4. Bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. Each pathogen can causes us to get sick and are all cured differently. Examples of each are listed below: Bacteria: pink eye, whooping cough, strep throat, TB, Lyme’s disease, most foodborne illness, bacterial pneumonea Virus: colds, influenza, chicken pox, measles, mono Fungi: athlete’s foot Protozoa: dysentery, malaria Spreading of Pathogens Spread of pathogens can be caused by many things including: food not properly cooked, water, direct and indirect contact with pathogens. Stopping Pathogens Diet, exercise, washing hands, cleaning surfaces, safe food preperation Immune System Responsible for keeping us healthy. Can be boosted by good sleep, exercise, and eating. Vitamin C is the most important vitamin for immune system. If immune system is weakened, our bodies cannot fight off disease as well. Anitbiotics Used for bacterial infections and diseases. They are very effective in curing disease, but our becoming less effective over time. They are less effective because bacteria are beginning to evolve and avoid being killed by antibiotics. This is due to overuse of the drugs. They are prescription drugs that are often prescribed too often. Farmers feed them to animals to keep them healthy, which causes antibiotics to end up in our food.