Fighting Disease
advertisement

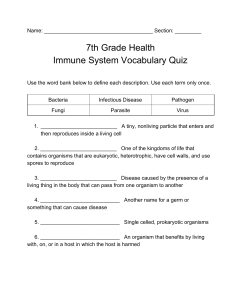
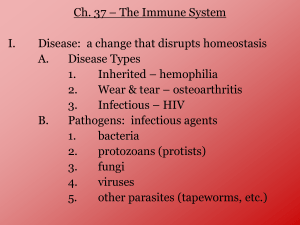
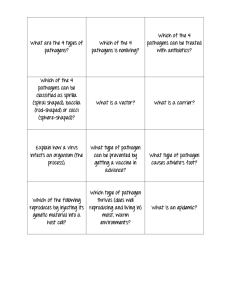
Fighting Disease Pathogen • An organism that causes diseases • All infectious diseases are caused by pathogens • When you have an infectious disease a pathogens have gotten inside your body and caused harm 4 major pathogens 1. Bacteria-damage cells by producing a toxin (tetanus, strep throat) 2. Viruses- destroy cells as they reproduce inside (flu, colds) 3. Fungi- athletes foot, ringworm 4. Protists- malaria, African Sleeping Sickness, dysentery. Spread of Pathogens - Infected people- directly (kissing) or indirectly (sneezing, coughing) - Soil, food, water- contagen in the food, soil, or water - Contaminated object- indirect contact - Infected animals- ticks, mosquitoes, raccoons, etc (biting a person) The Body’s Defenses • Skin is first line of defense • Breathing passages have cilia • Mouth and stomach have chemicals to destroy pathogens Immune system response • White blood cells- phagocyte (engulfs pathogen) • Inflammation- Increases blood flow to infected area (white blood cells) • Fever- Pathogens can’t grow at higher temperatures • TCells- distinguishes one pathogen from another Immune system cont.. • B Cells- Produce proteins that help destroy pathogens (antibody) • Antibodies bind to the pathogen and stop it from making you sick AIDS • Caused by the virus HIV • Attacks T cells and shuts down the immune system • Body loses ability to fight disease • Spread by body fluids- not shaking hands, hugging, toilet seat etc… Immunity • Active- bodies response to presence of pathogens. - result of getting the disease or a vaccine • Passive- Antibodies come from another source other than body (immunity passed from mother to baby at birth) Cancer • Non-infectious • Cells multiply uncontrollably • Carcinogen- cancer causing agent (tar in cigarette, uv radiation in sunlight) Vaccination • Antibodies and memory cells form • When real pathogen enters the body the memory cells help produce antibodies to fight it Antibiotic • Slows growth or kills bacteria • Totally ineffective against viruses Vector • Carries the disease but does not actually have the disease (ticks, mosquitoes) Carrier • Has the disease but shows no sign of the disease (some people carry strep throat but never have any symptoms) • Are still contagious even without symptoms