File
advertisement

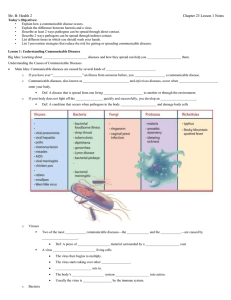
Guided Notes Standard 1: Objective 1 I can identify the 5 types of pathogens that cause communicable disease. I have a full understanding of what communicable diseases are. Key Vocabulary 1. Communicable Disease: A disease that is spread from one living thing to another or through the environment. 2. Pathogen: An organism that causes disease. 3. Infection: A condition that occurs when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and damage body cells. 4. Viruses: A form of genetic material that invades living cells to reproduce. 5. Bacteria: Single­celled microorganisms. 6. Toxin: A substance that kills cells or interferes with their functions. 7. Vector: An organism, such as a tick, that carries and transmits pathogens to humans or other animals. Notes Causes of Communicable Disease: ­ organisms that cause disease are called pathogens ­ there are five different types of pathogens: ­ viruses ­ bacteria ­ fungus ­ protozoans ­ rickettsias ­ infections happen when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and damage body cells ­ diseases develop because the body is unable to fight off infection Viruses ­ the most common viruses are the flu and the common cold ­ viruses alone are inactive; they need living cells to reproduce ­ after a virus gets into a cell, known as the host cell, the virus will take over that cell in order to make more viruses ­ viruses usually run their course and eventually are killed by the immune system ­ antibiotics do not work against viruses Bacteria ­ can be both good and bad ­ bacteria in digestive system help digest food and make vitamins ­ some bacteria produce toxins which kill cells ­ bacteria are usually destroyed by the immune system ­ most bacterial diseases can be treated with antibiotics Other Types of Pathogens 1. Fungi: plantlike organisms, such as molds and yeasts. Usually cause disease of the skin, mucous membranes, or lungs. 2. Protozoans: single­celled organisms that are larger and more complex than bacteria; most are harmless 3. Rickettsias: resemble bacteria; mostly enter humans through insect bites How Communicable Diseases are Transmitted 1. Direct Contact: direct contact with infected person, animal, or something in the environment ­ touching, biting, kissing, sexual contact ­ sneezing and coughing saliva and mucous into someone’s eyes, nose, or mouth ­ pregnant women may infect unborn child through the placenta ­ puncture wound from rusty object, such as a nail 2. Indirect Contact: without being close to an infected person 1. Contaminated objects : a person with a cold sneezes on a table or into their hand and then touches the table; you can contract the infection if you touch the table and then touch your mouth, nose, or eyes. 2. Vectors: Mosquitos take in pathogens when they feed on infected person; mosquito then injects those pathogens into the next person it bites 3. Water and food: undercooked meat, cross contamination, contaminated water supply 3. Airborne Transmission: Pathogens from a sneeze or cough float in the air for a long time and travel a long way; you don’t have to be close to the person to inhale their pathogens.