Communicable Diseases: Causes & Pathogens
advertisement

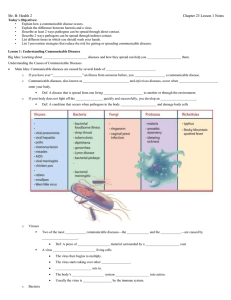
12.1 Notes – Causes of Communicable Diseases • • • • • disease – any condition that interferes with the proper function of the body or mind communicable disease – (contagious) a disease that can be spread to a person from another person, an animal, or an object noncommunicable disease – not contagious germs – organisms that are so small that the can be seen only through a microscope Are all germs bad for you? – no 12.1 Notes – Causes of Communicable Diseases • • • pathogens – the germs that are responsible for causing disease infection – a condition that occurs when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and damage body cells 4 types of pathogens: 12.1 Notes – Causes of Communicable Diseases • 4 types of pathogens: 1. viruses – the smallest and simplest diseasecausing organism 2. bacteria – tiny one-celled organisms that live nearly everywhere 3. fungi – primitive life-forms, such as molds or yeast, that cannot make their own food (athlete’s foot) 4. protozoa – one-celled organisms that have a more complex structure than bacteria 12.1 Notes – Causes of Communicable Diseases • 2 microscopic pathogens: 1. viruses 2. bacteria • 2 macroscopic pathogens: 1. fungi 2. protozoa 12.1 Notes – Causes of Communicable Diseases • Pathogens and the diseases they cause: – Viruses: • AIDS, chicken pox, colds, hepatitis, herpes, influenza, measles, mononucleosis, mumps, polio, rabies, smallpox, viral pneumonia – Bacteria: • Bacterial pneumonia, diphtheria, most foodborne illnesses, gonorrhea, Lyme disease, pinkeye, step throat, tuberculosis – Fungi: • Athlete’s foot, ringworm – Protozoa: 12.1 Notes – Causes of Communicable Diseases • How can pathogens spread? – – – – Getting bitten by an infected animal Sexual contact Sharing blood Drinking or eating something after someone is sick – E-coli, food poisoning – Kissing, touching – Sneezing, coughing