Disease & Pathogens
advertisement

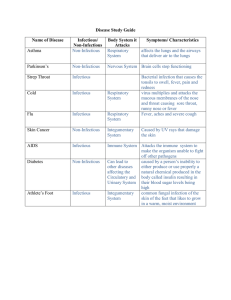
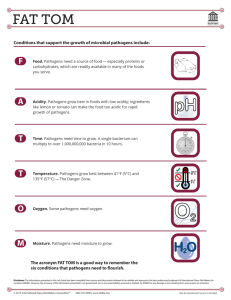
Disease & Pathogens Awareness & Prevention What are Pathogens • Pathogens are disease causing organisms. There are 5 types of Pathogens: - ______________ – smallest, toughest pathogens - _____________ – single celled organism, most plentiful and most pathogenic - ___________ – single or multi-celled organisms with thread like fibers and reproductive spores - __________ – single cell, microscopic animals that destroy cells by releasing enzymes and toxins to interfere with cell function. - Helminths (___________) – small parasitic worms that attack specific tissues or organ and compete with the host for nutrients. Virus vs Bacteria Virus Bacteria No cure – but treated with _________ medicines (reduces it’s affects) (__________ are antiviral) Cured with ___________ Unable to ____________ on it’s own ______________ on it’s own in ideal environment Take over cell’s __________ __________ and instructs it to produce new viral particles which are released to enter other cells Release __________ that digest body cells or toxins that produce specific effects MOST COMMON: MOST COMMON: __________ (is a Retrovirus) __. ________ _____________ and __________ – causes colds and respiratory infections Listeria, ____________, Tetanus, ____________ Influenza – the Flu Salmonella, Herpes, Hepatitis, _____________ Infectious vs Non-Infectious INFECTIOUS DISEASE NON-INFECTIOUS DISEASE Caused by __________ Caused by __________, _________, and lifestyle factors _______________ (Passed from Human to Human or Animal to Human) ___-______________ (Cannot be passed from one person to another, except through heredity) Acquired through ___________ activation Develops ______ _______ Some can be cured with ___________ ____________, but can be __________ with medication Communicable vs Non-Communicable COMMUNICABLE NON-COMMUNICABLE Passed from one __________ to ____________ Cannot be _________ from person to person Infectious Non-Infectious Acute onset/ Acquired from ___________ organism ___________ COMMON DISEASE: COMMON DISEASE: _______, Flu, Chicken Pox, Meningitis, HIV/AIDS, Herpes, Diabetes, ____________, Cancer, Arthritis, Polio, Pnuemonia, __________, Athlete’s Foot, SARS, _______ _______, Eating Disorder, Bone Disease, Rubella, ___________, Mumps, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis, Multiple Sclerosis, Muscle & _____ Disorders ____________ (________), Strep Throat, Whooping Cough Preventing the Spread of Communicable Disease • _______ your _________ frequently – especially if you’ve been around someone who is sick or has some type of bacterial or viral infection • Use a _____, the inside of your shirt/jacket, or the inside of your elbow to __________ your nose and mouth when you cough or sneeze instead of your ________. • Always use _______ ____ such as gloves, _______, masks to cover your skin, mouth, nose and eyes when coming in contact with another person’s ______ ______ such as blood, vomit, ______, urine, etc. • Stay at ______ if you are sick to keep from passing your germs onto others. • _________ items or areas where a person who has been sick has been in contact with. • Don’t be _______ fools! That’s _____! You’ll get ____!