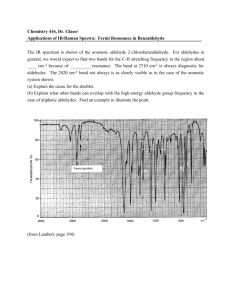
Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones
advertisement

CHAPTER 13: ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Before you can learn about aldehydes and ketones, you must first know something about the nomenclature of carboxylic acids since many of the names of aldehydes and ketones are derived from the names of the corresponding carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids: R-COOH, R-CO2H, Common names: HCO2H formic acid formica ant CH3CO2H acetic acid acetum vinegar CH3CH2CO2H propionic acid “first salt” CH3CH2CH2CO2H butyric acid butyrum butter CH3CH2CH2CH2CO2H valeric acid valerans ALDEHYDES COMMON NAMES STEM PLUS ALDEHYDE R-CHO R-CO2H HCH O HCO2H FORMALDEHYDE FORMICA - ANTS CH3CHO ACETALDEHYDE CH3COOH ACETUM - SOUR CH3CH2CHO PROPIONALDEHYDE PROTOS PION - FIRST FAT PROPIONIC ACID CH3CH2CH2CO2H BUTRYM - BUTTER CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO CAPROALDEHYDE ACETIC ACID CH3CH2CO2H CH3CH2CH2CHO BUTYRALDEHYDE FORMIC ACID BUTYRIC ACID CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CO2H CAPER - GOAT CAPROIC ACID NAMING ALDEHYDES IUPAC: Replace -e with -al. The aldehyde carbon is number 1. If -CHO is attached to a ring, use the suffix carbaldehyde. 4 Cha pter 18 O H C H H3C Common Formaldehyde IUPAC Methanal Cl H3C O O 2-Chloropropanal Acetaldehyde H H3CH2CH2C H Butanal O C C Butyraldehyde Propanal HO H C Propionaldehyde Ethanal O CH H3C CH2 H O O H 3-Hydroxypropanal H3CHC=HC C 2-Butenal H NOMENCLATURE Aromatic aldehydes are usually designated as derivatives of the simplest aromatic aldehyde, Benzaldehyde. O O H H OH H H O 2N Benzaldehyde O O p-Nitrobenzaldehyde o-Hydroxybenzaldehyde H3CO p-Methoxtbenzaldehyde KETONES: STRUCTURE AND NOMENCLATURE General formula: RCOR’ (R and R’=alkyl or aryl) Common name: listing the alkyl substitutents attached to the carbonyl group, followed by the word ketone. IUPAC system: relpace the ending –e by the suffix –one. The chain is numbred in such a way as give the lowest number to the C=O group. O H3C C O CH3 Common Dimethyl ketone IUPAC H3C C O C6 H 5 Methyl phenyl ketone Acetone Acetophenone Propanone Phenyl ethanone H3C C O CH=CH 2 H5C6 Methyl vinyl ketone C C6H5 Diphenyl ketone Benzophenone 3-Buten-2-one Diphenylmethanone O CH3CH2CCH3 ethyl methyl ketone O CH3CH2CCH2CH3 diethyl ketone O CH3CCH2CH2CH3 methyl n-propyl ketone (o)phenones: O R C Derived from common name of carboxylic acid, drop –ic acid, add – (o)phenone. O C benzophenone H3C O C acetophenone O O C2 H 5 O OH C C2 H 5 CHO O O C2 H 5 O OH CHO C C2 H 5 Cyclopentylpropanone 3-Ethyl-2-hydroxycyclohexanone 5-Oxohexanal BOILING POINTS More polar, so higher boiling point than comparable alkane or ether. Cannot H-bond to each other, so lower boiling point than comparable alcohol. 13 => Cha pter 18 SOLUBILITY Good solvent for alcohols. Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of carbonyl can accept a hydrogen bond from O-H or N-H. Acetone and acetaldehyde are miscible in water. 14 => Cha pter 18 Aldehydes synthesis 1) oxidation of primary alcohols: RCH2-OH + K2Cr2O7 (potassium dichromate) RCH=O+ H2 RCH2-OH + C5H5NHCrO3Cl RCH=O+ H2 (pyridinium chlorochromate, or PCC) [With other oxidizing agents, primary alcohols RCOOH] Aldehyde synthesis: Primary alcohols CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH K2Cr2O7, special conditions! 1-pentanol CH2OH CH3CH2CH2CH2CH=O pentanal valeraldehyde C5H5NHCrO3Cl CH=O pyridinium chlorochromate benzyl alcohol CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH + K2Cr2O7 1-pentanol benzaldehyde CH3CH2CH2CH2CO2H pentanoic acid Aldehyde synthesis: 2) reduction of acid chloride R O C LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 Cl lithium aluminum hydride tri-tert-butoxide O LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 Cl isovaleryl chloride R O C H O H isovaleraldehyde O LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 C Cl benzoyl chloride CH3 O CH3CHCH2C Cl isovaleryl chloride O C H benzaldehyde LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 CH3 O CH3CHCH2C H isovaleraldehyde Ketone synthesis: 1) oxidation of secondary alcohols H O OH NaOCl cyclohexanone cyclohexanol OH CH3CHCH3 isopropyl alcohol K2Cr2O7 H3C O C CH3 acetone Ketone synthesis: 2) Friedel-Crafts acylation AlCl3 RCOCl, AlCl3 + ArH O CH3CH2CH2C Cl + AlCl3 O R C Ar + HCl O CH3CH2CH2C butyrophenone Aromatic ketones (phenones) only! O C Cl O C AlCl3 + O2N O2N m-nitrobenzophenone O C Cl AlCl3 + NR NO2 Friedel Crafts acylation does not work on deactivated rings. ACETALS ANDHEMICETALS Acetal: two –OR groups bonded to the same carbon Hemiacetal: one –OR group and one –OH group bonded to the same carbon ENOLIZATION Keto-Enol Tautomerism Tautomerism: interconversion between two structures that differ by the placement of an atom or group Slow in neutral conditions, sped up in acid or base catalyzed systems Enol content is very small, <<<1% for most aldehydes and ketones