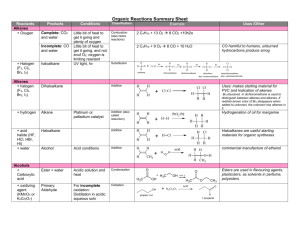
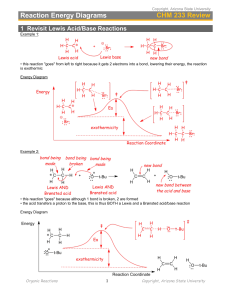
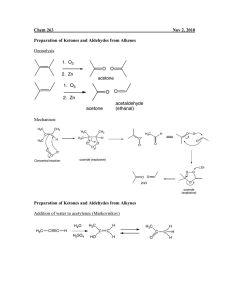
Answers
advertisement

CHM 112 1. SPRING 2007 WORKSHEET FOR ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Write the IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: H2 C H2 C CH H3C CH 3 CH 3 C CH 3 H2 C O C H CH CH 3 H 2 C C H2 C C H2 CH 3 C H2 O CH 3 CH 3 O 3-methyl-2-hexanone 3-isopropyl heptanone 3, 3-dimethyl octanal H2 C H3C H2 C C H2 C O O C H 3-cyclobutyl propanal 2. H2 C 1-phenyl-2-butanone Write the full or condensed structural formula for each of the following compounds: 2-ethyl cyclopentanone 2-chloro-3, 5-dimethyl heptanal benzaldehyde Cl H2 C CH 2 H3C H C H C CH CH 3 4-phenyl-2-octanone O C H CH 3 O O CH CH CH 3 3-hydroxy-butanal OH H C CH O H2C C H3C C H2 3. H2 C CH C H2 a. Aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols all have oxygen in their structures. Explain why the boiling points of alcohols are higher than the boiling points of corresponding (about same molar mass) carbonyls. Alcohols can hydrogen bond with each other because of the H H O C CH C hydrogen has a slightly positive charge and the oxygen a H C C C H H slightly negative one. The hydrogens on aldehydes or X H O C ketone are not significantly positive so there is no hydrogen H C C H bonding. Overcoming strong IMF’s like hydrogen bonding requires more energy and therefore a higher boiling point. 2 3 3 2 H2 C H 3C 2 OH C H2 O CH 3 C H2 2 HO C H2 3 b. Why are aldehydes and ketones more soluble in water than corresponding ethers? The aldehydes and ketones have an oxygen that is more accessible to the hydrogens in water to form hydrogen bonds. In an ether, the oxygen is less accessible and so hydrogen bonding is not as easy and therefore the molecule is less water soluble. 3-hexanone 4. propoxypropane Complete the following reactions with the most appropriate reactant(s) or product(s). H2 C H2 C CH H3C H2 C K2Cr2O7 CH 3 C H2 H2 C H3C CH 3 C C H2 OH O H2 C H3C 2+ Cu H2 C CH3 C No reaction because a ketone cannot be oxidized under these conditions C H2 O KMnO4 O OH CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 H2 C H3C H2 C O C C H2 CH 3 Cu2+ CH 3 C H H3C C C H2 O C CH 3 OH CH 3 H2 C H3C CH 3 C H H3C C C H2 H 3C CH 3 OH OH CH 3 C H2 CH 3 H2 C O C C C H2 [H] CH 3 H2 C H2 C O C C H2 CH 3 [H] H3 C O C C H2 CH 3 C H