Aldehydes, Ketones, and carboxylic acids
advertisement

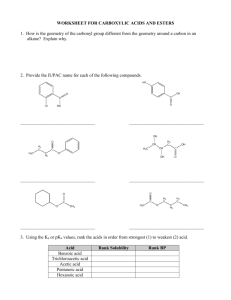
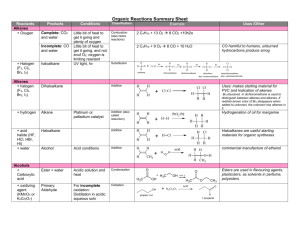
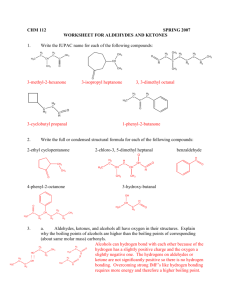
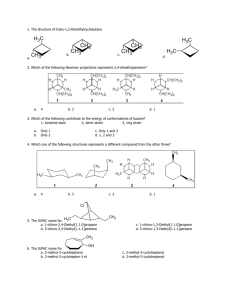
Aldehydes, Ketones, and carboxylic acids Aldehydes O R H The term Aldehyde come for the words alcohol dehydrogenation. Carbonyl group Preparation: Oxidation of primary alcohols according to the following equation: R OH + [O] R O Note: Oxidation can be considered as removal of hydrogens. [O] can be obtained from oxidazing agents such as KMnO4,KCr2O7,CuO. Aldehydes Examples: OH H Methyl alcohol O H + [O] Formaldehyde H H OH H3C Ethyl alcohol O H3C + [O] Acetaldehyde H H O CH3 H + [O] Toluene Benzaldehyde Aldehydes Note: The formation of acetaldehyde in the liver is partailly responsible for liver cirrhosis. The formation of formaldehyde and ist oxidation product formic acid are responsible for the systematic toxicity of methyl alcohol (methanol). The side chain in toluene is more susceptible to oxidation than the benzne ring. IUPAC Nomenclature of Aldehydes The aldehyde group is always at the end of the chain (carbon 1) Aldehydes end in al Take the name of the longest chain cotaining the aldehyde group Drop the ending e and replace it by al Br H3C CH3 O H3C H3C 6-bromo-5,7-dimethyloctanal H3C O Cl Br 3-bromo-5-chloro-4-methylhexanal IUPAC Name Common Name Methanal Formaldehyde Ethanal Acetaldehyde Propanal Propionaldehyde 2-Methylpropanal Isobutyraldehyde Uses of aldehydes O H O O H H OH OCH3 Formaldehyde Vanillin Cinnamic adehyde 40% Formaldehyde in water (Formalin): used for disinfection of excerta, rooms, clothing (Mechanism: hardening of proteins), in embalming ( )التحنيطwater, and as preservative for biological specimens. Benzaldehyde: preparation of flavoring agents, parfums, drugs, and dyes. Vanilllin (Vanilla beans) and cinnamic aldehyde (cinnamon bark): flavoring agents. Tests of aldehydes Adehydes are good reducing agents. Glucose contains an aldehyde group. Therefore, it can react as an aldehyde, and can be detected in urin using special solutions such as Benedicts, Fehlings, or Tollens reagent. Reactions of aldehydes Oxidation: Acid O O R + [O] R OH H Reduction: Alcohol O R + [H] H OH R H Examples: H3C Ethanal O + [H] O H3C Ethanol OH OH + [H] Benzaldehyde Benzylalcohol Reactions of aldehydes Biological oxidation-reduction reactions in the are crried out in the body by substances called coenzymes. One coenzyme is NAD+(Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) H3C OH + NAD+ H3C O + NADH Ketones Secondary alcohol oxidation ketone CH3 + [O] H3C O HO Isopropyl alcohol 2- Propanol O CH3 Acetophenone CH3 H3C Cl O Acetone Propanone Cl Chloracetophenone (tear gas) Naming of Ketones IUPAC Aldehydes end in -one Take the name of the longest chain Drop the ending e and replace it by -one Common Each alkyl group attached to the carbonyl group is named and the word ketone is added afterward. O H3C 3-Hexanone Ethylpropylketone CH3 H3C CH3 Cl Cl O 4,4-dichloro-2-pentanone Uses of Ketones Acetone is a good solvent for fats and oils (previuosly used in finger nail polish). Present in small amounts in blood and urine (in normal individuals). Present in large amounts in blood and urine and expired air in case of untreated diabetes mellitus. Dihydroxy acetone is an intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism. O O H3 C CH3 Acetone HO OH Dihydroxy acetone Reactions of ketones Ketones are usually unreactive. Ketones are not easily oxidized. They can however be reduced to the corresponding secondary alcohols. Ketones give negative tests with oxidazing agents such as Benedict‘s reagent. However aldehyde give positive results with these reagents. Reactions of ketones Hemiacetals and Hemiketals How can an acetal or a ketal be formed? Importance: Hemiketal / acetal monosaccharides Ketal / Acetal Di- and Polysaccharides Carboxylic acids Preparation Oxidation of aldehydes H3C O + [O] Acetaldehyde H3C O Acetic acid HO O + Benzaldehyde HO O [O] Benzoic acid Stepwise oxidation of a primary alcohol carboxylic acid H3C OH Methylalcohol + [O] H2C O + [O] Formaldehyde O HO Formic acid Direct oxidation of primary alcohols acids HO H3 C OH Ethyl alcohol + [O] H3 C O Acetic acid Naming of carboxylic acids IUPAC Names Carboxylic acids end in –oic acid Take the name of the longest chain cotaining the acid group. Drop the ending e and replace it by -oic Common Names Derived from the names of the aldehyde forms from which they may be prepared HO H3 C O Ethanoic acid Acetic acid Carboxyl group which yields hydrogen ions Naming of carboxylic acids Dicarboxylic, and tricarboxylic acids are carboxylic acids which contain two and three carboxylic acids, respectively. O O HO O HO O HO Ethanedioic aic Oxalic acid OH O Propanedioic acid HO Malonic acid OH O OH Butanedioic acid Succinic acid O O OH OH Citric acid O OH Naming of carboxylic acids Examples: O H3C H3C OH CH3 Cl 2-chloro-3,4-dimethylheptanoic acid HO O Cl Br 4-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid Properties and Reactions of Carboxylic acids Weak acids O O H3C H+ + OH H3C O- Acetic acid Hydrogen ion Acetate ion React with bases to form salts and water O O H3C + NaOH OH CH3CHOOH + NaOH H3C - + O Na + H2O CH3CHOONa + H2O Properties and Reactions of Carboxylic acids React with bases to form salts and water CH3CHOOH + NaHCO3 CH3CHOONa + CO2 + H2O Sodium bicarbonate 2 HCOOH + Na2CO3 Formic acid Sodium carbonate 2 HCOONa + CO2 + H2O Sodium formate Their solubility in water decreases as the length of their carbon chains increases React with alcohols to form esters Medically important acids Magnesium citrate cathartic (evacuation of bowel) Sodium Citrate anticoagulant (removel of Ca2+ needed for coagulation Lactic acid results from fermentation of milk sugar (lactose) [lactic acidboth acid and alcohol) Lactic acid is formed by anarobic energy production in the body from Pyruvate (muscle exercise) Pyruvic acid is formed during anarobic phase of glucose oxidation Pyruvic acid acetyl CoA Krebs cycleEnergy production O OH O O H3 C H3 C OH OH Lactic acid Pyruvic acid Medically important acids Oxalic acid removal of strains, from clothing, prevention of blood clotting (Note: Oxalic acid is a poison if taken internally) Stearic acid (C18) is a fatty acid, insoluble in water, ist salt is used as in Soap Bezoic acid antifungal; sodium salt preservative Salicylic acid (both alcohol and acid) removal of warts and corns Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin): OH HO O analgesic, antipyretic, aginst O rheumatic fever ( الحمى )الروماتيزمية, prevention of blood OH O CH3 clots from forming (Note: contraindicated after Surgery) O helps in preventing heart attacks, bleeding of stomach Acetylsalicylic (not to be taken on empty Salicylic acid acid stomach)