element of fiction - Adame
advertisement

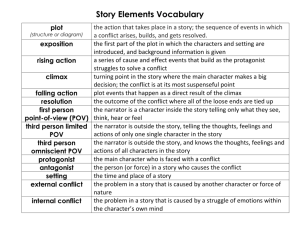
ELEMENTS OF FICTION Plot, Characters, Setting, Theme, and Point of View Ms. Adame 8 th Grade Language Arts Parts of a Fictional Story •All fictional stories have •Plot •Point of View •Setting •Characters •Theme •Mood/Tone Plot Vocabulary 1. plot: series of actions and events of a story. 2. conflict: a struggle between two opposing forces. Conflict causes the action. 3. exposition: introduction to the story; it gives background information that is necessary to understand the story. It consists of• characters: who or what the story is about • setting: time and place of the story • basic problem: the main problem of the story (the main character wants something, but someone or something gets in the way.) 4. rising action: sequence of events leading up to the climax. Suspense begins to build/things get interesting. 5. climax: the turning point; the most interesting part of the story. Something happens that changes the plot; the main character changes in some way. 6. falling action: sequence of events leading to the conclusion. The conflict begins to get resolved. 7. resolution: the end or conclusion. All the loose strings are tied together. Plot Diagram (copy in composition book) THE TURNING POINT Climax Exposition Resolution Plot Analysis of Boy Named Sue •Exposition: 1. Characters: Sue and Dad 2. Setting: Gatlinburg in mid July 3. Basic problem: Sue hates his name and wants to get revenge against his father for naming him Sue, but he does not know where his father is. •Rising Action 1. A boy is named Sue by his father 2. The father abandons his wife and child 3. Sue grows up being teased about his name 4. Sue becomes a fighter 5. Sue vows to find and kill his father 6. Sue finds his father playing cards in a saloon in Gatlinburg Plot Analysis of Boy Named Sue (continued) •Climax: Sue approaches his father and says, “My name is Sue! How do you do! Now you’re gonna die!” •Falling Action 1. 2. 3. 4. Sue and his father fight Sue and his father pull guns on each other The father explains his reasoning behind naming him Sue The father says Sue should thank him for making him tough •Resolution: Sue sees his name from a new perspective and throws down his gun. He decides not to kill his father, but resolves to give his own son a better name. Plot Diagram Sue approaches his father and says, “My name is Sue! How do you do! Now you’re gonna die!” Climax Exposition Resolution Point of View An automobile accident occurs. Two drivers are involved. Witnesses include four sidewalk spectators, a policeman, a man with a video camera who happened to be shooting the scene, and the pilot of a helicopter that was flying overhead. Here we have nine different points of view and, most likely, nine different descriptions of the accident. In fiction, who tells the story and how it is told are critical issues for an author to decide. The tone and feel of the story, and even its meaning, can change radically depending on who is telling the story. Remember, someone is always between the reader and the action of the story and is telling the story from his or her own point of view. This angle of vision, the point of view from which the people, events, and details of a story are viewed, is important to consider when reading a story. Point-of-View •The view from whose eyes the story is being told (where you place the camera) •There are three major types of point-of-view First Person •the story is told from the viewpoint of one character who narrates the story. •Pronouns “I,” “me,” and “my” are mostly used. •Key element: Narrator is a character in the story. Narrator is not reliable. Third Person Limited •Uses an outside narrator who is not involved in the story. •Pronouns used are mostly “he,” “she,” and “they.” •Key element: Narrator does not know what is in other characters’ minds. Narrator can only tell what is observable about other characters. Third Person Omniscient •The narrator is not a character in the story. •Pronouns mostly used are also “he,” “she,” and “they.” •Key element: This narrator has access into ALL characters’ minds and can tell what they are ALL thinking, feeling, and doing.