Matter of state_II(download)
advertisement
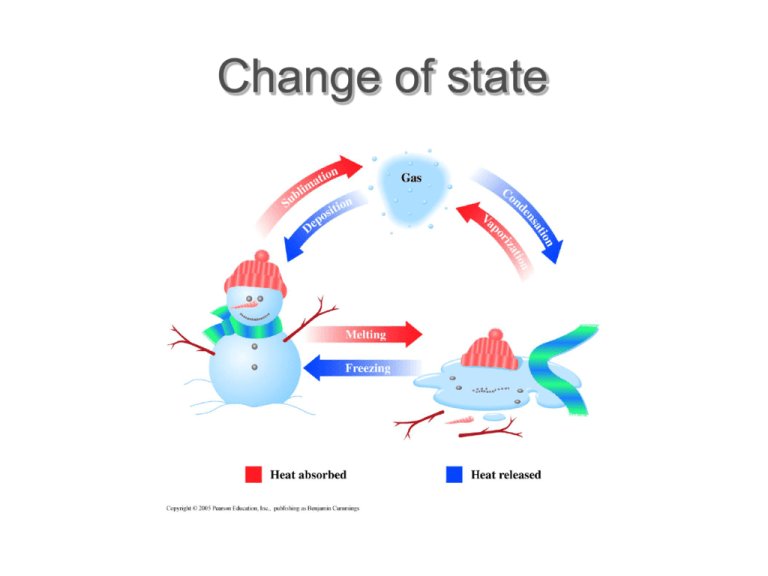
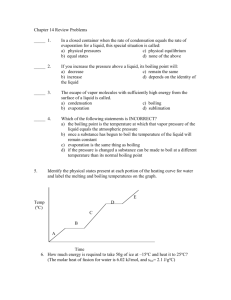
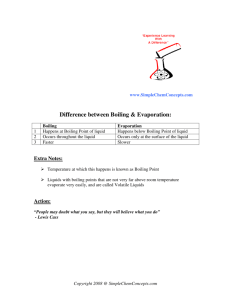
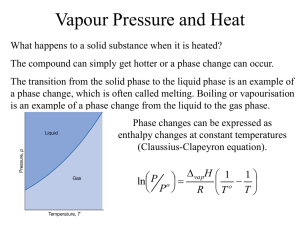
Change of state Change of state and energy consumption Fusion Heat of fusion is energy required to convert the solid into the liquid at the same temperature Originally called latent heat because no temperature rise occurs Freezing releases same quantity of heat Vapour pressure There is always a certain pressure of a gas in equilibrium with the liquid phase, even at temperatures well below the boiling point Consequence of range of energies of molecular motion Vapour pressure and boiling Molecules do not all have the same energy High energy molecules escape the liquid – vapour pressure When vapour pressure = atmospheric pressure boiling occurs Sublimation is direct transition of solid to gas (dry ice) Molecular energy and change of state Combining of molecules generates heat condensation Input of energy breaks molecular bonds vaporization Sublimation Solid converts directly to a gas “Dry ice” – solid carbon dioxide sublimes to the gas at room temperature Boiling Heat of vaporization is energy required to convert liquid into vapor at the same temperature Condensation releases the same quantity of energy Heat, temperature and change of state At phase change, no change in T Heat input in boiling much greater At phase change, no change in T Evaporation requires greater heat input than melting because of the greater number of bonds to be broken We lick our fingers to extinguish a burning candle Energy calculations Calculate heat required to convert 15.0 g water at 25.0ºC to steam at 100ºC. Calculation is sum of two parts: 1. Heating the liquid 1. Mass water 2. Temperature change 3. SH water 2. Boiling the liquid 1. Heat vaporization water 2. Mass water State change calculation Calculate heat required to convert 15.0 g water at 25.0ºC to steam at 100ºC. SH water = 4.18 J/gºC, ΔHvap = 2,259 J/g