Page Advanced Chemistry Notes 1.2 Properties of Matter 1.2a
advertisement

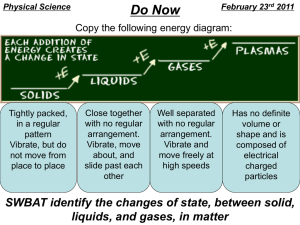
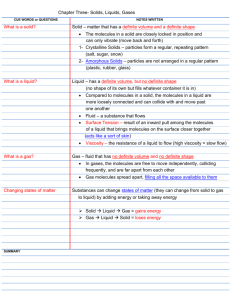
Advanced Chemistry Notes 1.2 Properties of Matter 1.2a Properties of Matter Physical Property – can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substance Ex: States of matter, temp, mass, density, solubility Water starts freezing @ 0oC (32oF)(273 K), and water starts to boil @ 100oC (212oF)(373 K) Chemical Property – can be observed only by changing the composition of the substance Ex: flammability, reactivity, and explosiveness Intensive Property – does not depend on the amount of material present Ex: density, color, odor, taste, boiling point, freezing point Extensive Property – depends on the amount of material present Ex: mass, length, volume, energy 1.2b States of Matter Solid – rigid; definite shape and volume; molecules close together vibrating about fixed points virtually incompressible Liquid – definite volume but takes on the shape of the container; molecules vibrate and can slide past one another BUT are still close together slightly compressible Gas – no definite volume and takes on the shape of the container; molecules vibrate, are independent of each other VERY far apart highly compressible Plasma - a gas made up of ions and electrons Ex: lightning, fluorescent lights, stars Bose-Einstein Condensate - matter formed when temperatures are only a few billionths of a degree above absolute zero Believed to have existed in the early universe, and possibly exists now in the outer layers of neutron stars; Future uses: quantum computing Vapor – the gas phase of a substance that is normally a solid or liquid at room temperature Fluid – that can flow; gases and liquids 1.2c Phase Changes Vaporization – liquid to gas Evaporation - vaporization at the surface of a liquid Boiling - vaporization throughout the liquid Melting - solid to liquid Freezing - liquid to solid Condensation – gas to liquid Sublimation – solid to gas Deposition - gas to solid Page 1 1.2d Observations in Chemistry Qualitative – observations that deal with descriptions of the material Quantitative – observations that deal with measurements of the material Advanced Chemistry Notes 1.2 Practice Problems 1. What is the main difference between physical properties and chemical properties? a. Chemical properties are cooler than physical properties b. Chemical properties are observed with the senses, physical properties are observed by changing the substance c. Physical properties are observed with the senses, chemical properties are observed by changing the substance d. There is no difference 2. Give one example of a physical property. 3. Give one example of a chemical property. 4. Circle whether each of the following is a physical change or a chemical change: a. Tearing a sheet of paper Physical Chemical b. Melting a piece of wax Physical Chemical c. Burning a log Physical Chemical 5. Label the following as a quantitative (N) or qualitative (L) observation by placing an N or L in the blank. ___a. The blanket is blue ___d. The reaction took 5 seconds ___b. The window is wide ___e. This quiz is cool ___c. He’s 5’9” tall ___f. This quiz has 6 questions Page 2 6. Contrast mixtures with pure substance.