Chemical vs. Physical Changes
advertisement
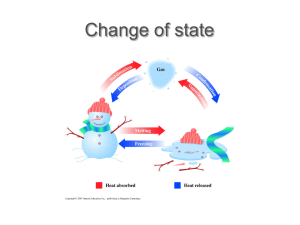
Chemical vs. Physical Changes Physical Changes, P. 68-72 Physical changes involve altering the form of a substance, but does not change it to another substance. Ex: bending a nail, tearing paper, making playdough changing states of matter – boiling water, freezing popsicle, mixing koolaid, etc… Chemical Changes Defined During a chemical change, matter is changed into a new substance with new properties. Ex: burning wood – wood to ash and gases Other examples: baking a cake, glow sticks, making toast, mixing vinegar and baking soda, milk ‘curdling’, etc… Think of a chemical change of when you can’t change the new substance back to it’s original form. Law of Conservation of Matter Matter is not created or destroyed in any chemical or physical change. Mass of reactants always equals the mass of the products Energy and Change During physical and chemical changes, energy is either added or taken away. Thermal energy is energy from molecule movement (heat) Chemical energy is the energy from the bonds between molecules in a substance. Law of conservation of energy – during any chem. Or phys. Change, amount of energy stays the same. Examples of conservation of Energy Unlit match contains chemical energy When lit – energy converted to thermal and light energy. Amount of energy remains the same, just changes form. Changes of State All changes of state are physical changes. All state changes involve loss or gain of thermal energy Liquid to Gas State Vaporization is when a liquid gains enough thermal energy to become a gas – molecules move faster. Evaporation – vaporization only occurs on the surface. Ex: puddle drying up after a rain. Boiling – when vaporization happens throughout the liquid. Condensation When a gas loses enough thermal energy to return to a liquid, called condensation. Molecules slow down Ex: dew on grass in the morning. Clouds = water vapor cools at higher elevations, becomes liquid water. Sublimation Sublimation occurs when the surface particles of a solid gain enough energy to become a gas. Skip the liquid state. Ex: Dry ice – solid carbon dioxide. Dry ice made by putting carbon dioxide under extreme pressure, when reaches normal pressure, sublimates. Chemical Changes Chemical changes = chemical reactions In all chemical reactions, new substances are produced. All reactions either release or absorb energy. Ex: of absorption – plant growth, cold packs. Ex: of release – digestion, baking, lighting a match, burning wood