Ideal Gas Laws.ppt - christophersonbiology
advertisement

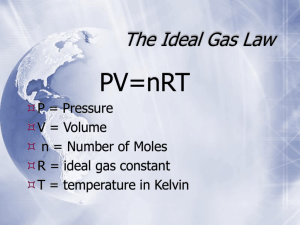
Wake-up 1. Write the formula for Charles Law. 2. Write the formula for Boyle’s Law. 3. Bromine gas has a pressure of 536.8 mmHg. When it is dispensed into a new container, its pressure becomes 784.6 mmHg with a new volume of 412.3 mL. What was the original volume? 4. Identify the Law for #3. Ideal Gas Laws What is the IDEAL GAS LAW? What are the variables involved? What is Avogadro’s Law and didn’t I already learn about him with the mole? What is an Ideal Gas? 1. Made up of molecules which are in constant random motion in straight lines. What is an Ideal Gas? 2. The volume of the molecules is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas What is an Ideal Gas? 3. All collisions are perfectly elastic. (There is no loss of kinetic energy during the collision.) Ideal Gas Law Equation Equation is on the Reference Table What is R? R is called the Ideal Gas Constant or Universal Gas Constant Gas Constant Value See Reference Table 0.0821 62.4 8.314 L atm mole K L mmHg mole K L kPa mole K What is the difference between each constant? Gas Constant Value See Reference Table 0.0821 62.4 8.314 L atm mole K L mmHg mole K L kPa mole K Units of Pressure – Select constant by units used in problem Proper units of Ideal Gas Formula When using the Ideal Gas Formula, use correct units!!! Check units before use equation. P = Pressure (atm) V = Volume (L) n = Number of moles (mol) R = Gas constant L atm mol K T = Temperature (K) Example #1 How many moles of N2 are in a 750 mL vessel at 26 degrees Celsius and 625 mm Hg? P = 625 mmHg V = 750mL 0.750 L n=? R = 62.4 L mmHg mol K T = 26°C 299 K (625)(0.75) = (n)(62.4)(299) 468.75 = (18657.6)(n) N = 0.025 mol Example #2 If I have 17 moles of gas at a temperature of 67 0C, and a volume of 88.89 liters, what is the pressure (kPa) of the gas? P = ? kPa V = 88.89 L n = 17 mol R = 8.314 L kPa mol K T = 67°C 340 K (P)(88.89) = (17)(8.314)(340) (P)(88.89) = (48054.92) P = 540.6 kPa Example #3 If I have 7.7 moles of gas at a pressure of 0.09 atm and at a temperature of 56 0C, what is the volume of the container that the gas is in? P = 0.09 atm V=? n = 7.7 mol R = 0.0821 L atm mol K T = 56°C 329 K (0.09)(V) = (7.7)(0.0821)(329) (0.09)(V) = (207.98) N = 2310.9 L