mixture hydrogen
advertisement

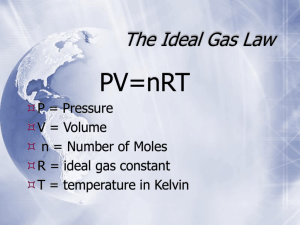
Tutorial questions (5th May 2014) Chemistry NS104 1. A mixture of hydrogen H2 (1.01 g) and chlorine Cl2 (17.73 g) in a container at 300 K has a total gas pressure of 98.8 kPa. What is the partial pressure of hydrogen and chlorine in the mixture? ANSWER: Moles of H2 =n= mass/molar mass = 1.02/2.02 = 0.500 mol Moles of Cl2 =n= mass/molar mass = 17.73/70.90 = 0.250 mol Total moles = 0.500 + 0.250 = 0.750 mol. Total pressure = 98.8 kPa. Partial pressure of each gas is proportional to its mole fraction in the mixture Therefore partial pressure of H2 and Cl2 is calculated with the following formula : P= Xn X Ptotal Where mole fraction is calculated as : XH = nH / ntotal = (0.500/0.750) =0.66 Xcl2 = ncl2 / ntotal = (0.250/0.750) = 0.33 PH= XH X Ptotal = 0.66 x 98.8 = 65.2kPa PCl2= XCl2 X Ptotal = 0.33 x 98.8 = 32.9kPa 2. What is the density (in g/L) of a sample of SO2 at 932 mmHg and 65°C ? (R= 0.0821 L . atm/ K . mol , 1atm= 760 mmHg) First convert units : T= 65C (converter to K) = 338K P= 932 mmHg (converted to atm) = 1.22atm Than, calculate the Molar mass of SO2, which is ≈ 64.1 g/ mol The formula for density (accroding ideal gas law) is : / d= P X M / R X T = 1.23 atm X 64.1 g/ mol 0.0821 L atm/ K mol . 338 K d= 2.84 g/L 𝑴= 𝒎𝑹𝑻 𝑷𝑽 = 𝒎𝑹𝑻 𝑽𝑷 = 𝒎 𝑽 𝒙 p= 𝑹𝑻 𝑷 𝑴𝑷 𝑹𝑻 Because Prepared by Jasmin Sutkovic 5th May 2014 =𝒑𝒙 𝒎 𝑽 =𝒑 𝑹𝑻 𝑷 , so we get