Naming Molecular Compounds: Formulas & Prefixes
advertisement

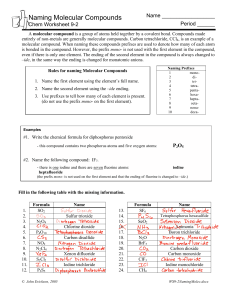
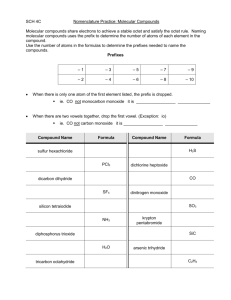
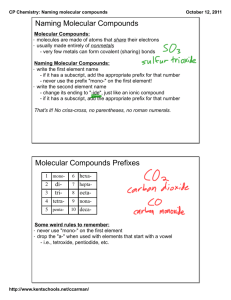
Chapter 9.3 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds Naming Binary Molecular Compounds In molecular compounds, both elements are nonmetals. The elements involved are not ions…ionic naming rules do not apply. Prefixes are used to distinguish compounds containing different amounts of the same two elements. The prefix in the name of a binary molecular compound tells how many atoms of each element are present in each molecule of the compound. Prefixes used are in table 9.4. CO is carbon monoxide. CO2 is carbon dioxide. N2O is dinitrogen oxide. The names of all binary molecular compounds end in –ide. The vowel at the end of the prefix is often dropped. Carbon monoxide, not carbon monooxide. Naming Guidelines Confirm compound is binary molecular. Name elements in order listed in formula. Use prefixes to indicate the number of each kind of atom. Omit mono- when the formula contains only one atom of the first element in the name. The suffix of the second element is –ide. Practice… SF6 sulfur hexaflouride Cl2O8 dichlorine octoxide Writing Formulas for Binary Molecular Compounds Simple. Use prefixes in the name to tell you the subscript of each element in the formula. Then write the correct symbols of the two elements with the appropriate subscripts. Practice…silicon carbide SiC dinitrogen tetroxide N2O4