IntroMolecular
advertisement
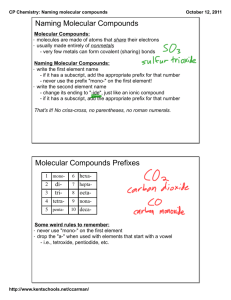
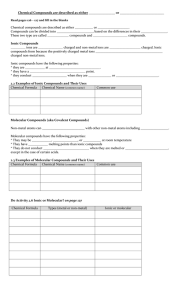
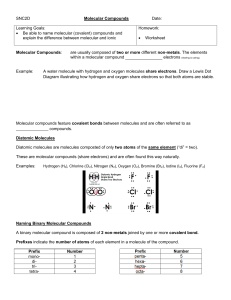
Science 10: Chemical Reactions NAMING & MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Naming, Naming, Formula?! Why is this important? IUPAC International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (est. 1919) Developed the system you are learning to ensure that each pure substance has a unique name (systematic name) What are some advantages of this system? Properties of Ionic Compounds Metal & Non-Metal Atoms held together with ionic bonds One element gains electrons (anion) One elements loses electrons (cation) Form large, repeating, cubic lattice structures Properties of Molecular Compounds Usually two non-metals Atoms joined by covalent bonds to form molecules Atoms share electrons like a “tug-of-war” Molecular compounds are made up of many molecules attracted to one another Naming Molecular Compounds 1. The first element in the name is usually the one that is farther left on the periodic table. 2. The suffix “-ide” is attached to the name of the second element 3. Prefixes are used to indicate the how many of each type of atom are present in one molecule (ex. mono-, di-, tri-) 4. Only use the prefix mono if it applies to the second element in the name Example How would we write the name of a compound that is one part C and one part O? Answer: carbon monoxide Example How would we write the name of a compound that is two parts N and three parts O? Answer: dinitrogen trioxide Writing Formula for Molecular Compounds Like in the name, the element that is farther left on the periodic table is listed first in the formula. Just like in the formula of ionic compounds, the formula of molecular compounds are written to show the ratio of one element to another with subscripts Example What is the formula for the compound nitrogen tribromide? Answer: NBr3 Example What is the formula for the compound disulfur difluoride? Answer: S2F2