Compound Name
advertisement
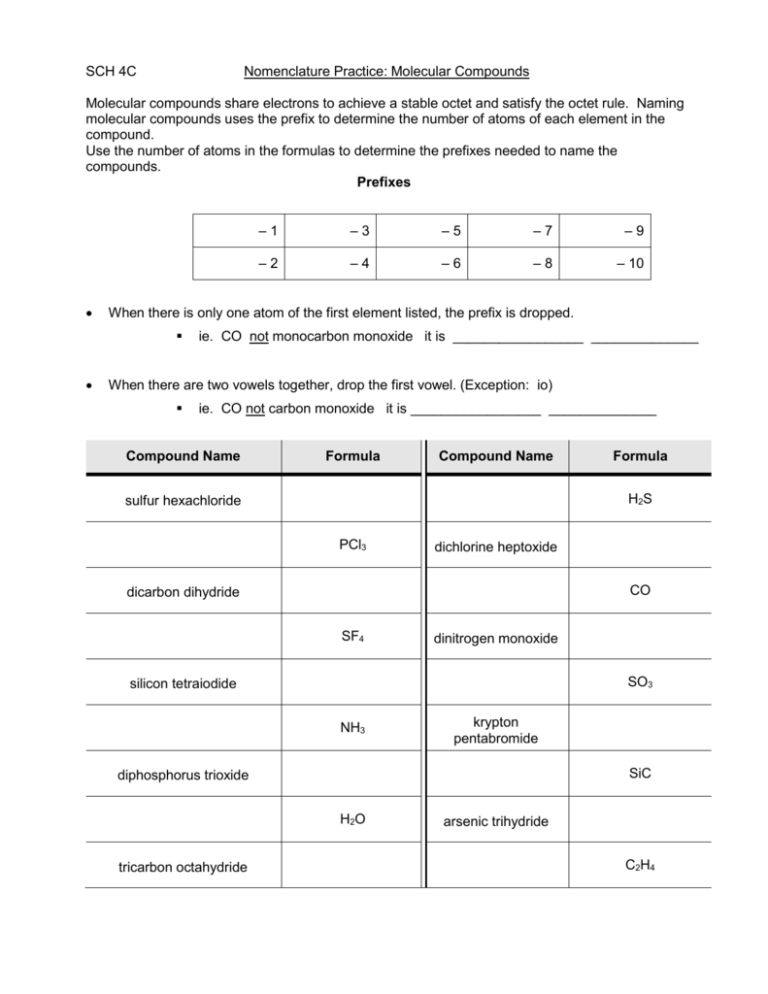
SCH 4C Nomenclature Practice: Molecular Compounds Molecular compounds share electrons to achieve a stable octet and satisfy the octet rule. Naming molecular compounds uses the prefix to determine the number of atoms of each element in the compound. Use the number of atoms in the formulas to determine the prefixes needed to name the compounds. Prefixes –3 –5 –7 –9 –2 –4 –6 –8 – 10 When there is only one atom of the first element listed, the prefix is dropped. –1 ie. CO not monocarbon monoxide it is _________________ ______________ When there are two vowels together, drop the first vowel. (Exception: io) ie. CO not carbon monoxide it is _________________ ______________ Compound Name Formula Compound Name H2S sulfur hexachloride PCl3 dichlorine heptoxide CO dicarbon dihydride SF4 dinitrogen monoxide SO3 silicon tetraiodide NH3 krypton pentabromide SiC diphosphorus trioxide H2O tricarbon octahydride Formula arsenic trihydride C2H4 AsBr3 trioxide N2O4 carbon tetrachloride SiO2 selenium dioxide Nomenclature Practice: Ionic & Molecular Compounds Fill in the boxes below, but be sure to determine if the compound is ionic or molecular first! If ionic, find the ion charges, then cross & drop. If molecular, use prefixes to determine the number of atoms. Name of Compound Formula ZnCO3 Name of Compound Ca(IO3)2 Pb(ClO2)4 MgO Ca(ClO)2 MgS H2 AuPO4 Aluminum hydroxide dicarbon tetrahyride NaHCO3 Cl2 Tin (II) nitrite NH3 sulfur hexafluoride Carbon tetrachloride Iron (III) cyanide PbI4 nickel (II) bromide Oxygen gas cesium phosphate Mg(ClO2)2 ammonium sulfate cadmium iodide potassium permanganate Formula N2O5 nitrite Ag3PO4 SeO2 Name of Compound barium aluminum chromate dichlorine heptoxide Formula dinitrogen monoxide cobalt (II) carbonate Cr(CN)3 Sn(SO4)2 sulfur trioxide